Basic Introduction and Principle of Tube Furnace
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-09-25 00:38
2024-09-25 00:38
In modern industry and research fields, high-temperature heat treatment technology plays a crucial role, and tube furnaces are one of the core equipment for achieving this technology. This article will explore the fundamental concepts and principles of tube furnaces, helping you better understand their structure, types, and wide-ranging applications.
Introduction to Tube Furnaces
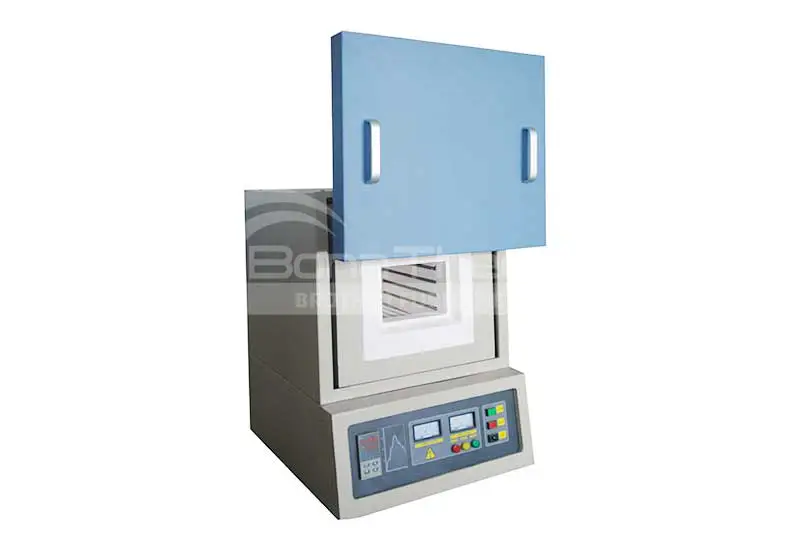
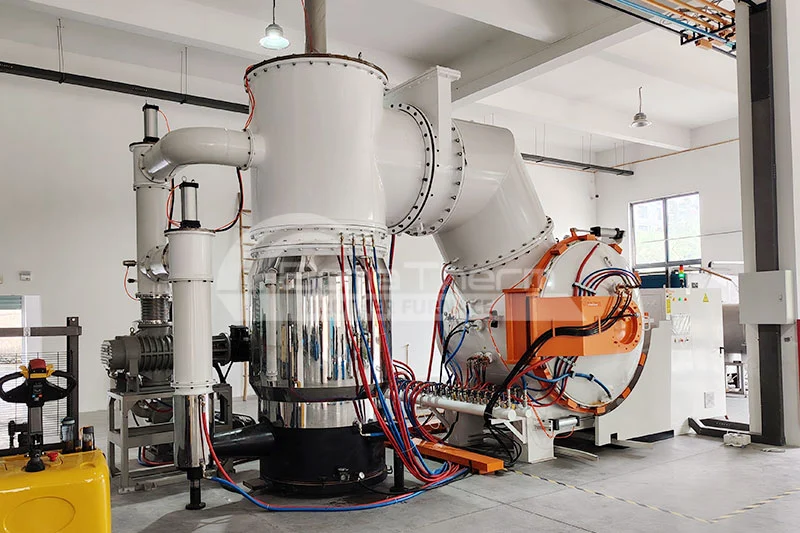
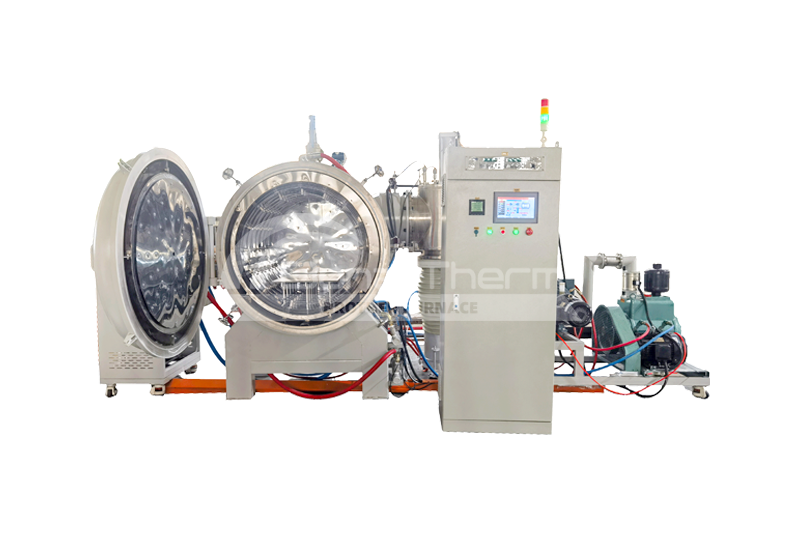
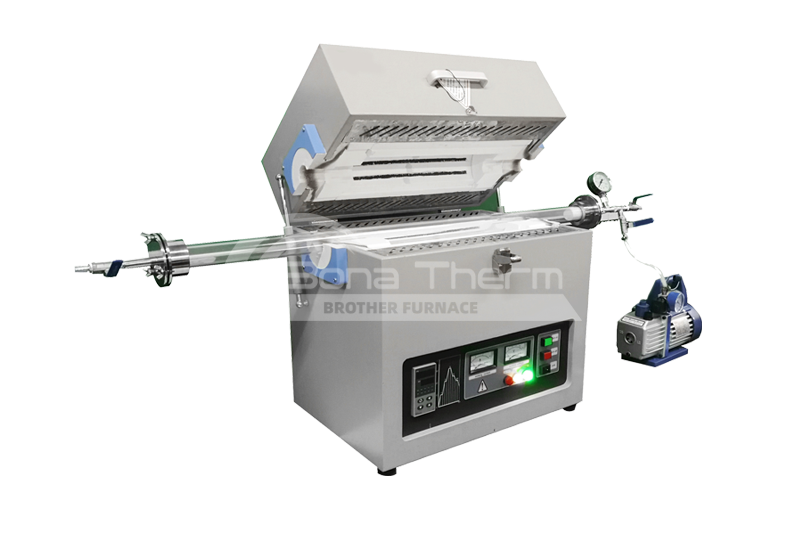
High-temperature tube furnaces are specialized heating devices designed to provide a uniform thermal treatment environment. They primarily consist of a heating tube, heating elements, gas inlets and outlets, and control systems. Tube furnaces are widely used in materials research, chemical synthesis, ceramic sintering, and metal heat treatment. They can also create vacuum environments—click here to learn more about vacuum tube furnaces. Brother Furnace tube furnaces can reach a maximum temperature of 1700°C, meeting various experimental requirements.
Basic Principles of Tube Furnaces
The operation of tube furnaces involves convection, radiation, and conduction. The heating elements are typically made of resistance wire or ceramic materials that generate heat when electrical current passes through them. The heat is then transferred from the furnace wall to the internal gas and samples, ensuring a uniform temperature distribution during heating. Additionally, tube furnaces can operate under vacuum or specific atmospheres, enhancing the heat treatment effect and preventing oxidation and contamination.
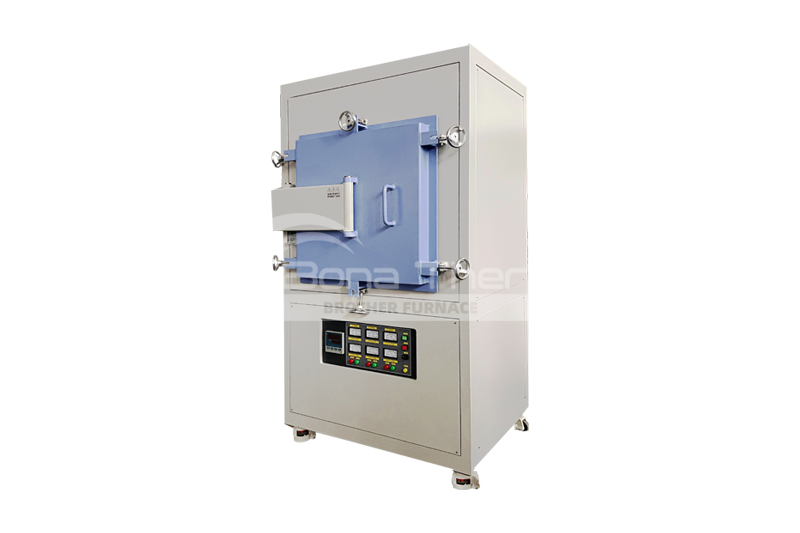
Common Types of Tube Furnaces
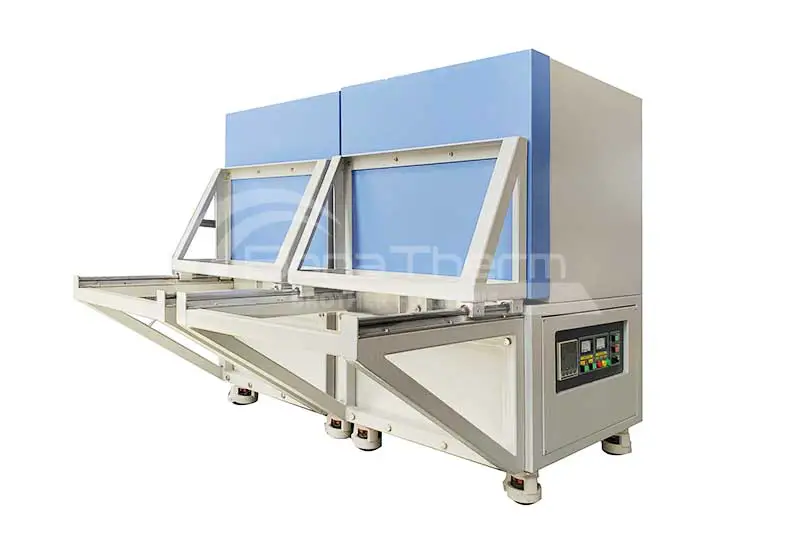
| Horizontal Tube Furnaces: Samples are placed horizontally, making them suitable for larger or longer samples. They are commonly used in industrial applications and large-scale experiments. |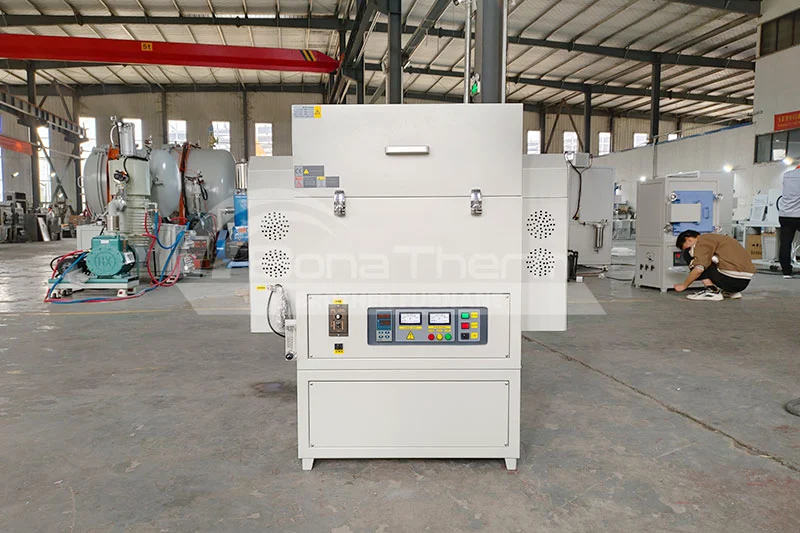  |
| Vertical Tube Furnaces: Designed for small samples, the vertical layout allows for smoother airflow, enhancing heating efficiency. These are ideal for atmosphere control and precise experiments. |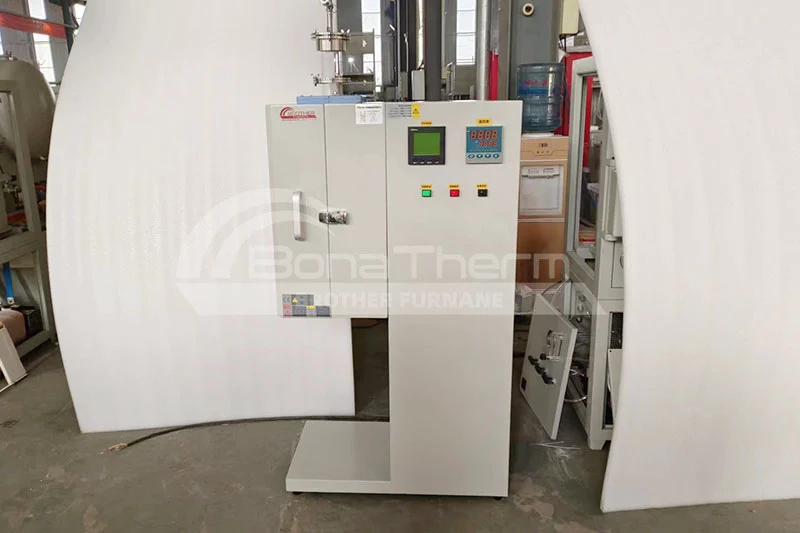  |
| Rotary Tube Furnaces: Samples rotate within the furnace to ensure uniform heating, often used for powder sintering and gas-phase reactions, improving treatment outcomes. |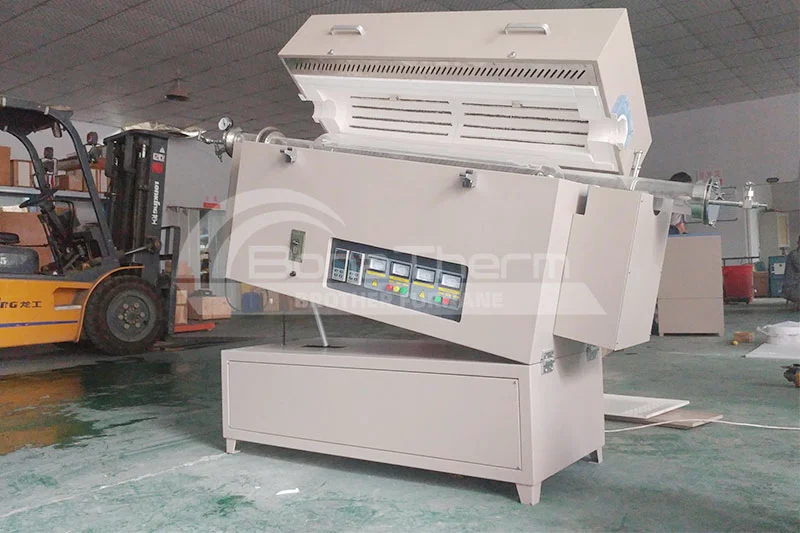  |
| Multi-Zone Tube Furnaces: Equipped with multiple heating zones, these furnaces allow for different temperatures to be set in various areas, suitable for complex heat treatment processes and ensuring optimal heating for each sample region. |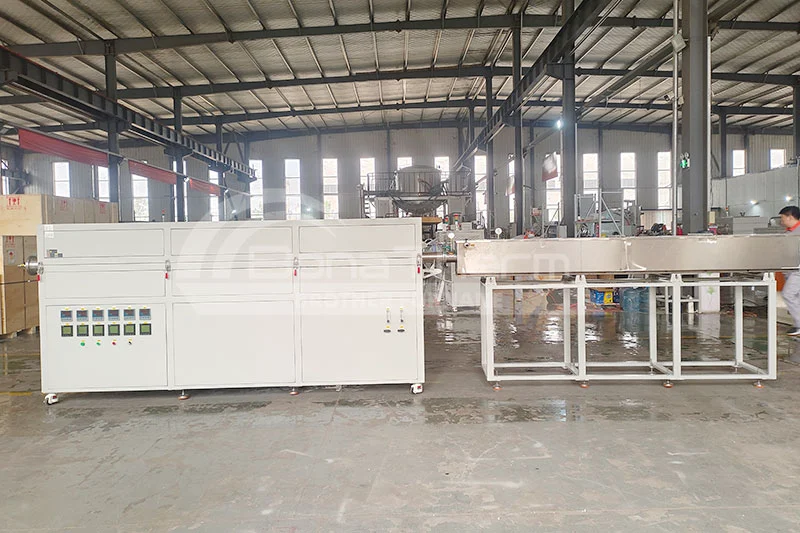  |
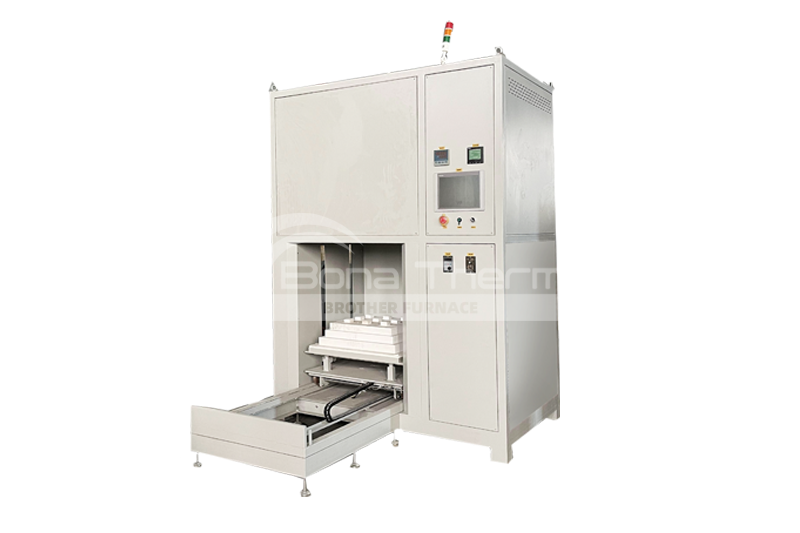
Brother Furnace can also customize tube furnaces based on specific customer needs, having previously developed CVD tube furnaces, sliding rapid-cooling tube furnaces, and dual-tube furnaces, among others.
Applications of Tube Furnaces
The applications of tube furnaces are extensive, including:
Materials Synthesis: Used for synthesizing new materials, particularly in high-temperature and specific atmosphere reactions.
Ceramic Sintering: Provides the necessary high temperatures and atmospheric conditions to ensure the quality and strength of ceramic products.
Metal Heat Treatment: Utilized for processes such as annealing, quenching, and aging to improve metal properties.
Semiconductor Processing: In the semiconductor industry, tube furnaces are used for the thermal treatment and surface processing of silicon wafers.
Catalyst Research: Employed in the preparation and testing of catalysts to optimize catalytic performance.
Tube furnaces are commonly found in laboratories, universities, research institutions, and various industrial sectors.
 |  |
Conclusion
With their efficient heating capabilities and flexible application characteristics, tube furnaces play an irreplaceable role in both research and industrial fields. Brother Furnace's tube furnaces can reach temperatures of up to 1700℃ and feature excellent temperature control and atmosphere regulation capabilities, ensuring users can conduct heat treatments under a variety of complex conditions. This makes them one of the most trusted choices on the market.
Order Brother Furnace tube furnace today to enhance the efficiency, precision, and reliability of your experiments and production processes!