What Materials Can Be Brazed with a Vacuum Furnace?
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-08-23 00:17
2024-08-23 00:17
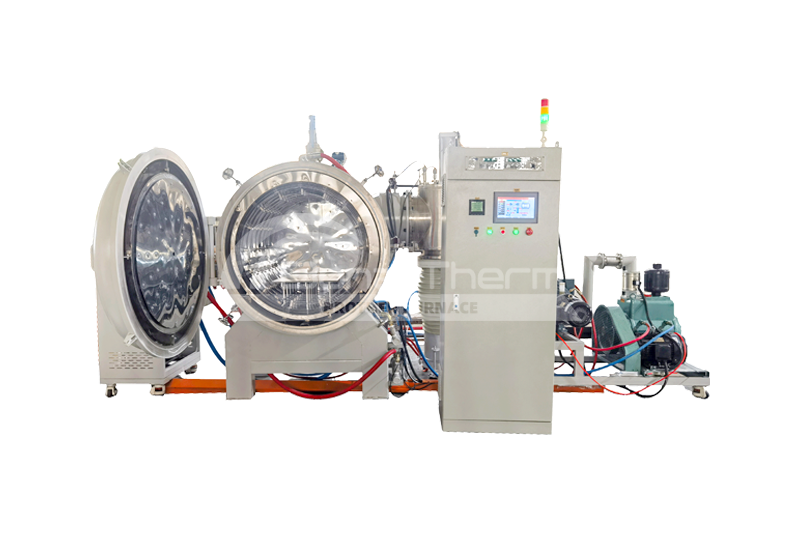
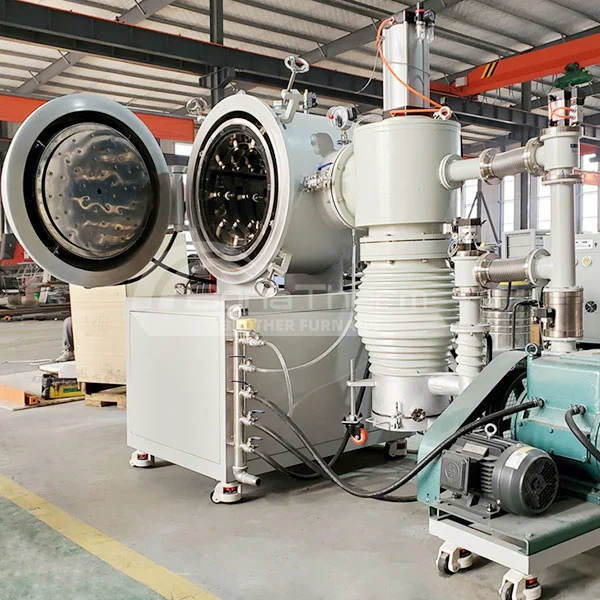
About Vacuum Brazing Furnace
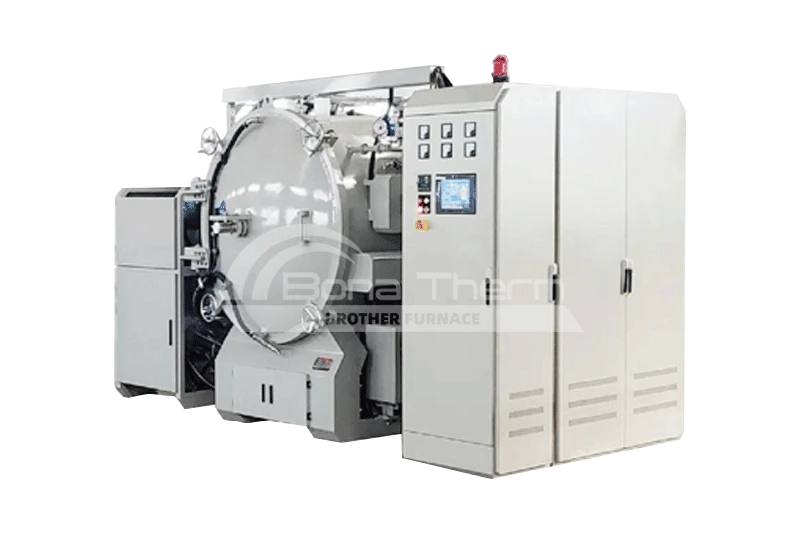
As one of the most advanced devices in the heat treatment industry, vacuum furnaces are highly regarded for their outstanding performance and wide-ranging applications. The vacuum brazing furnace, in particular, stands out as a prime example of precision brazing and heat treatment technology due to its exceptional performance in high-temperature and vacuum environments. So, which materials are suitable for brazing with a vacuum molybdenum foil furnace? Read on to find out.

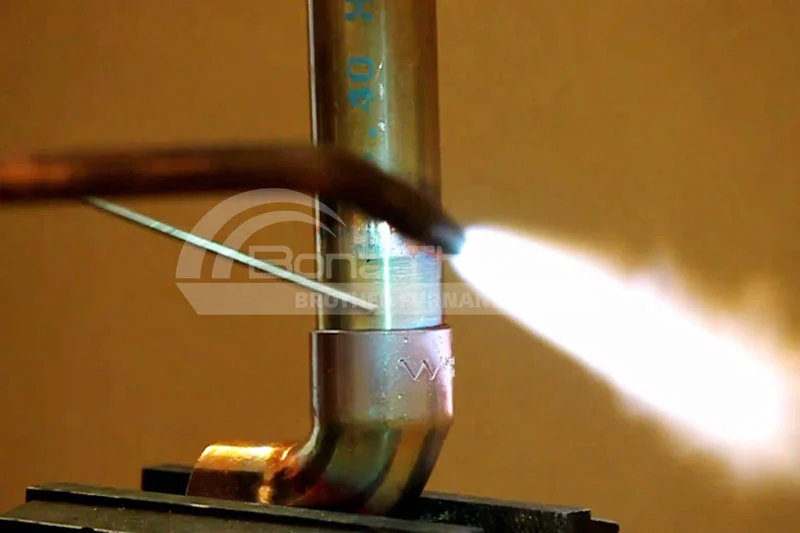
What is Brazing?
Let’s first understand the principle of brazing. Brazing is a metal-joining process that involves connecting two metal or other materials using a filler material (called brazing alloy) that is melted. Unlike welding, the base materials (the metals being joined) do not melt. Instead, the brazing alloy melts at a temperature higher than its melting point but lower than that of the base materials, forming a strong joint once cooled.The principle of using a vacuum furnace for brazing involves heating the workpieces in a vacuum environment, which causes the brazing alloy to melt and flow, creating a strong joint.

What Materials Can Be Brazed in a Vacuum Furnace?
Vacuum brazing furnaces can braze a variety of metal materials, including but not limited to aluminum, copper, stainless steel, titanium alloys, and high-temperature alloys. When brazing aluminum in a vacuum environment, oxidation issues are avoided, ensuring the strength and integrity of the joints. Copper and its alloys benefit from the oxygen-free environment of the vacuum brazing furnace, enabling high-quality connections suitable for electronic and electrical applications. Titanium alloys and high-temperature alloys, known for their excellent oxidation resistance and high-temperature performance, are commonly used for critical components in aerospace and high-tech manufacturing. The versatility of the vacuum brazing furnace makes it an ideal choice for handling complex and precision materials.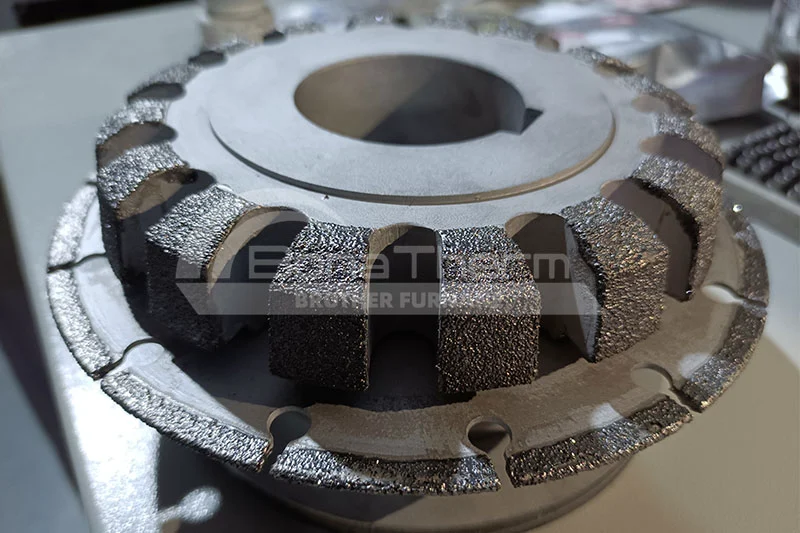
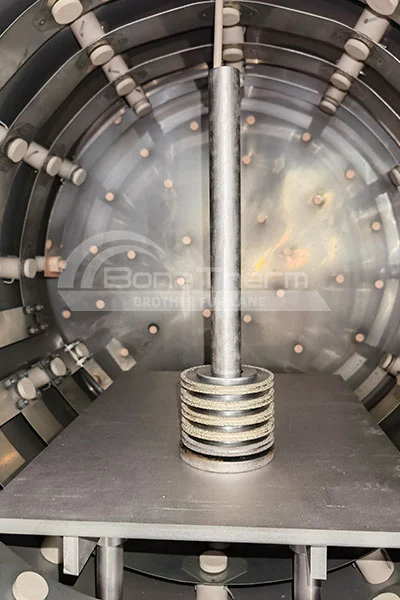

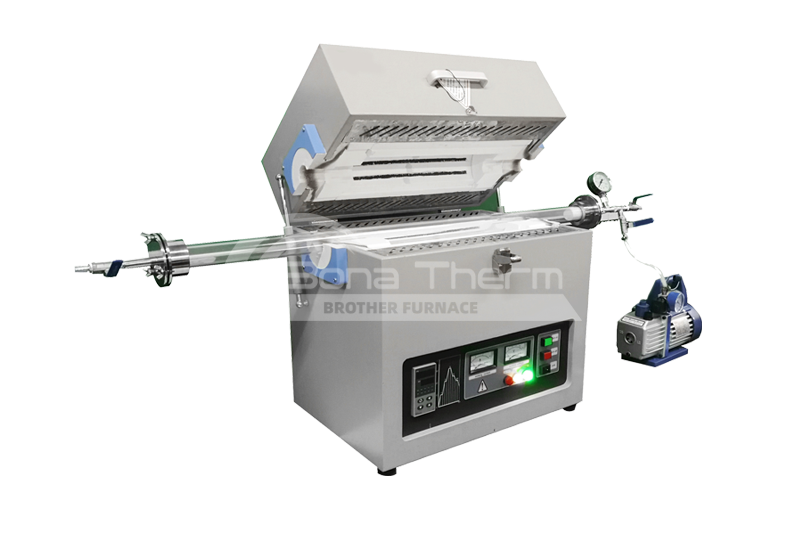
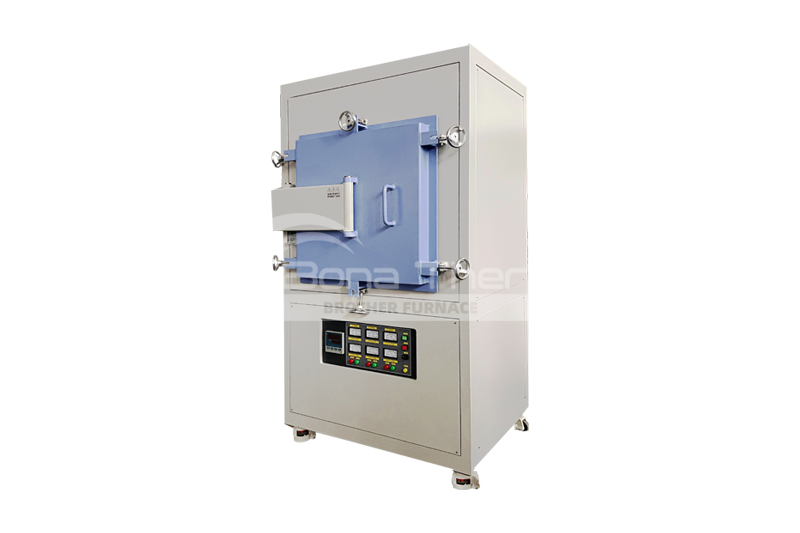
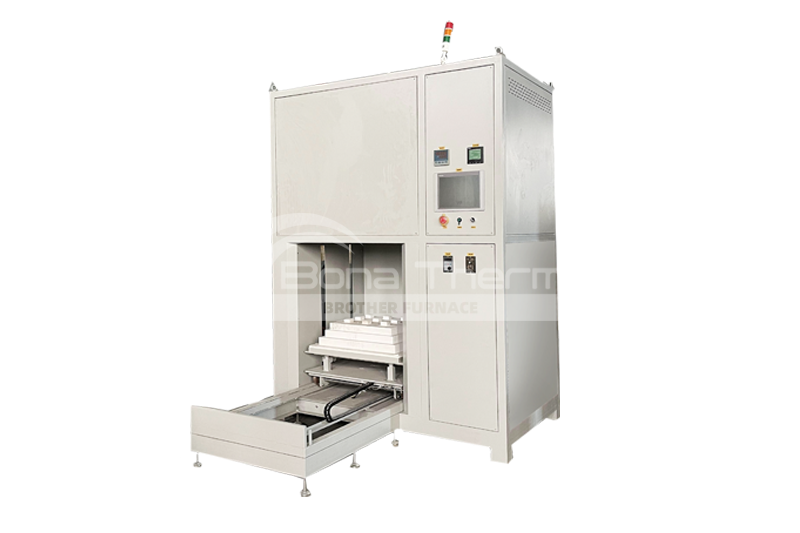
Other Applications of Vacuum Furnaces
In addition to brazing, vacuum furnaces can be applied to:Sintering: Vacuum furnaces are widely used for sintering high-temperature ceramics, metal powders, and alloy powders. The vacuum environment reduces oxidation and other gas reactions, leading to higher purity and performance of the materials during the sintering process.
Annealing: In metal processing, vacuum furnaces are commonly used for annealing processes to eliminate internal stresses, improve mechanical properties, and adjust the microstructure of metals.
Heat Treatment: Vacuum furnaces are used for various metal and alloy heat treatments, such as quenching, tempering, and surface hardening. The vacuum environment helps reduce contamination and oxidation, enhancing the treatment effectiveness.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): are used for depositing thin films and coatings. The vacuum furnace provides the necessary environment for depositing thin layers of material on substrates.
Melting: Used for melting high-purity metals like tungsten, molybdenum, and other high-melting-point materials. The vacuum environment prevents oxidation and contamination during the melting process.
Material Testing: In high-tech materials research and testing, vacuum furnaces simulate extreme environmental conditions to test the performance and durability of materials.
Materials Brazed with a Vacuum Molybdenum Foil Furnace