Introduction to Heating Elements in Vacuum Furnaces
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-07-01 20:17
2024-07-01 20:17
As a crucial thermal processing equipment in modern industry, the vacuum furnace's performance and application are heavily influenced by its heating elements. The selection of heating elements is critical to the furnace’s overall efficiency and effectiveness. This article provides an in-depth look at the types of heating elements used in vacuum furnaces and the criteria for selecting them, helping readers to make informed decisions.
What are the common heating elements for vacuum furnaces?
The following outlines the common heating elements used in vacuum furnaces, highlighting their advantages and the types of materials they are best suited for.
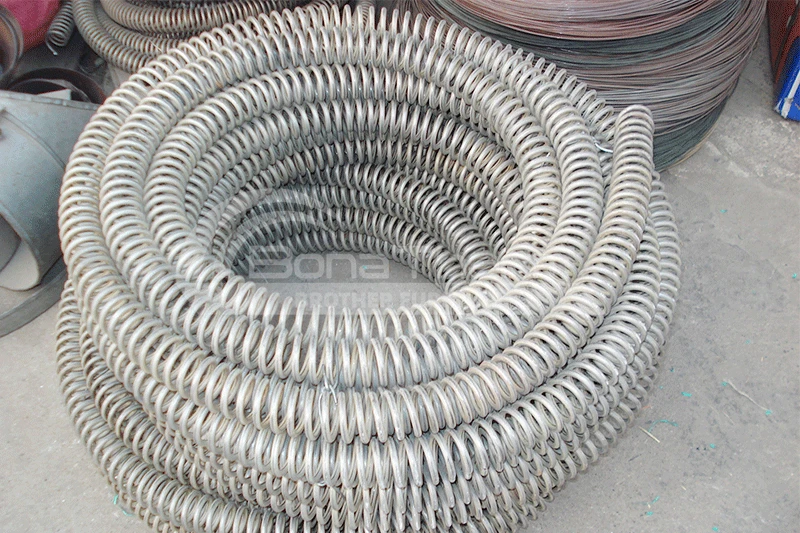 |  |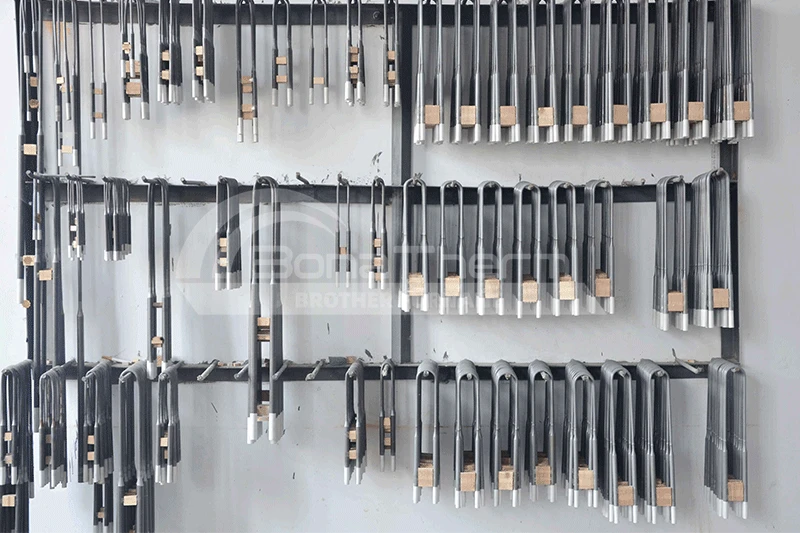  |
Advantages: Resistance wire heating elements offer good electrical resistance and thermal stability, are cost-effective, and easy to install and replace. Suitable Materials: Ideal for medium to low-temperature environments, such as industrial heat treatment and laboratory equipment. For instance, heating steel and non-ferrous metals. | Advantages: Silicon carbide rods have high electrical resistance and excellent thermal shock resistance, enabling stable operation in high-temperature environments. Suitable Materials: Suitable for high-temperature industries like semiconductors and ceramics. For example, semiconductors and ceramics. | Advantages: Silicon molybdenum rods possess excellent oxidation resistance and high-temperature stability, maintaining good performance at extremely high temperatures. Suitable Materials: Ideal for high-temperature environments such as ceramics and glass industries. Suitable for heating ceramics and glass. |
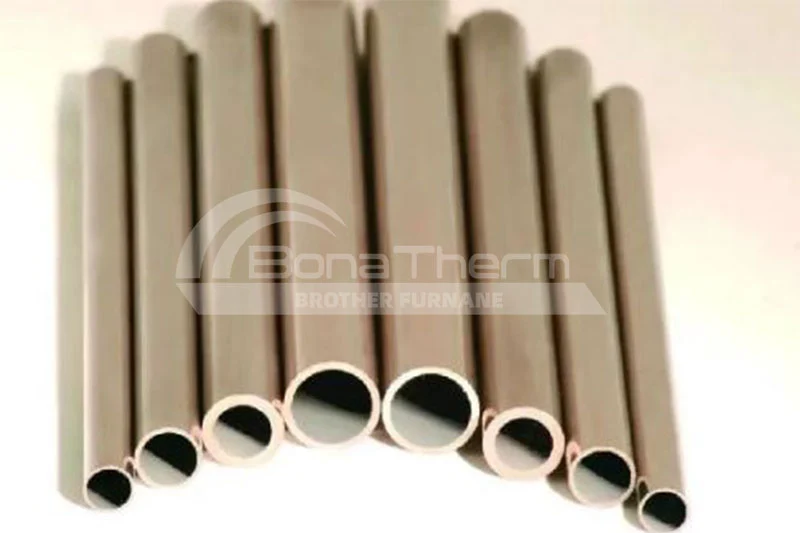 |  |  |  |
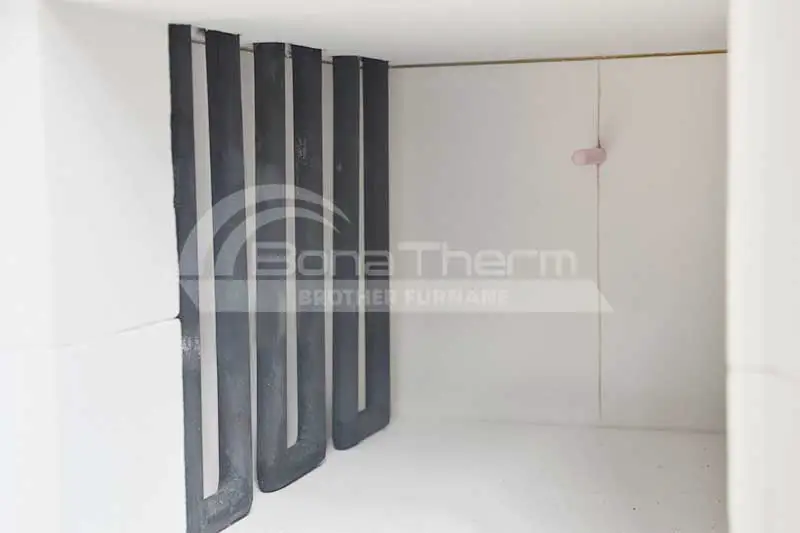
Advantages: Alloy heating tubes offer high electrical resistance and good oxidation resistance, with a long service life. Suitable Materials: Suitable for chemical equipment and metal heat treatment applications in medium to high-temperature environments. Ideal for heating metals and alloys. | Advantages: Molybdenum heating elements feature extremely high melting points and excellent thermal conductivity, ensuring stable operation in ultra-high temperature environments. Suitable Materials: Suitable for fields requiring extremely high temperatures, such as metallurgy and high-temperature heat treatment. For example, high-melting-point metals and special alloys. | Advantages: Graphite tubes provide high electrical conductivity and excellent corrosion resistance, enabling long-term use in high-temperature environments. Suitable Materials: Suitable for vacuum sintering and semiconductor industries. For example, carbon-based materials and refractory metals. | Advantages: Tungsten mesh heating elements feature extremely high melting points and good electrical resistance, ensuring stable operation in ultra-high temperature environments. Suitable Materials: Ideal for high-temperature industries such as metallurgy and aerospace. For example, high-melting-point alloys and special materials. |
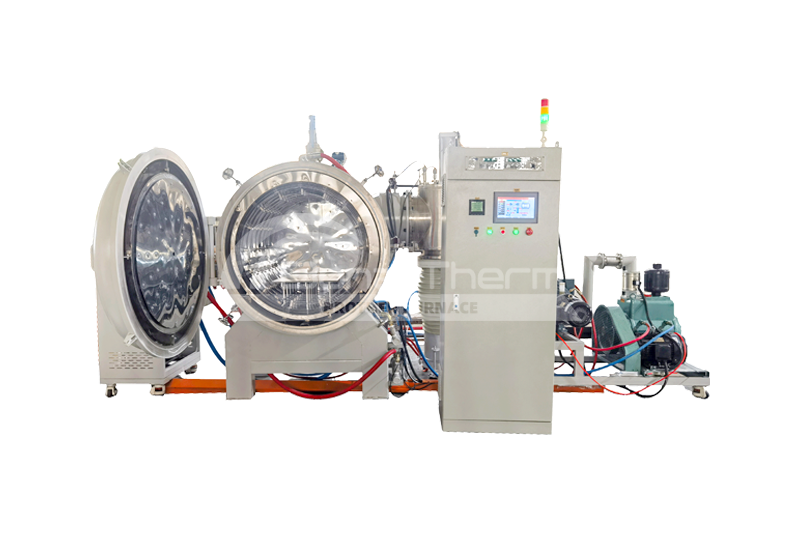
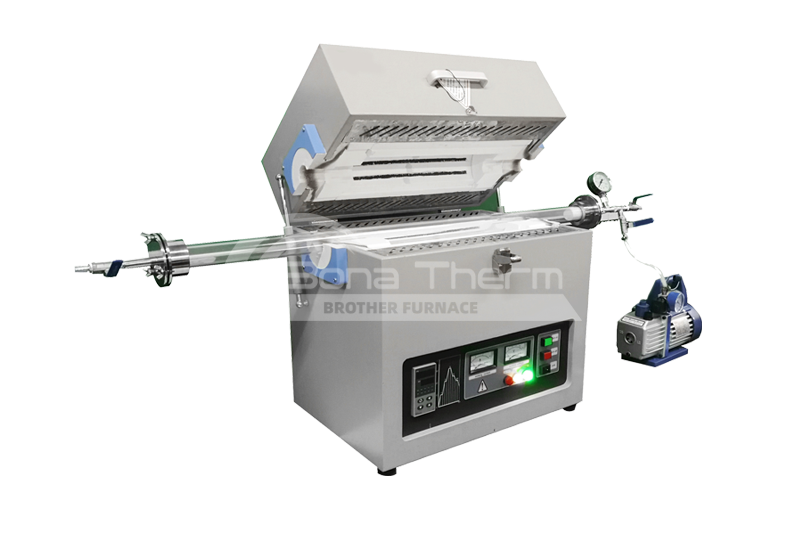
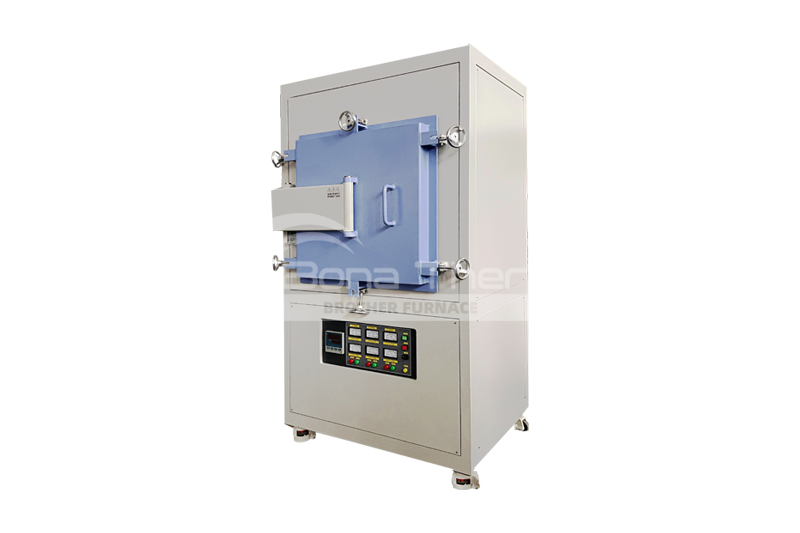
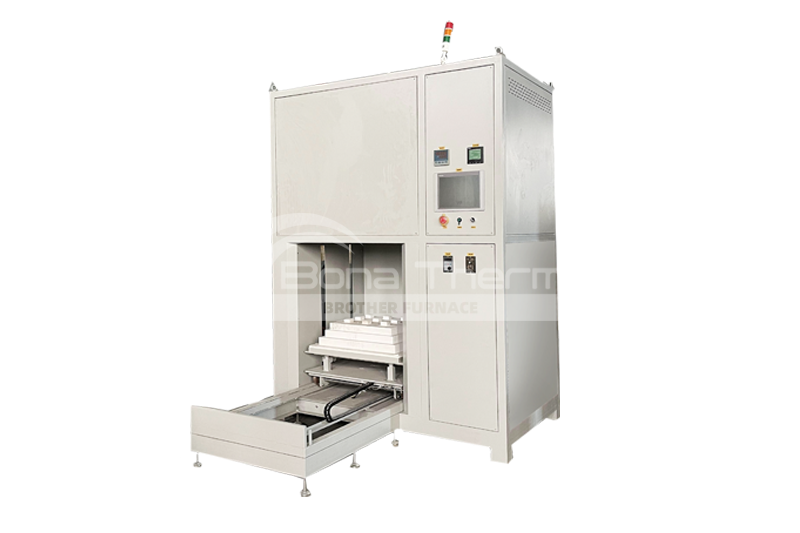
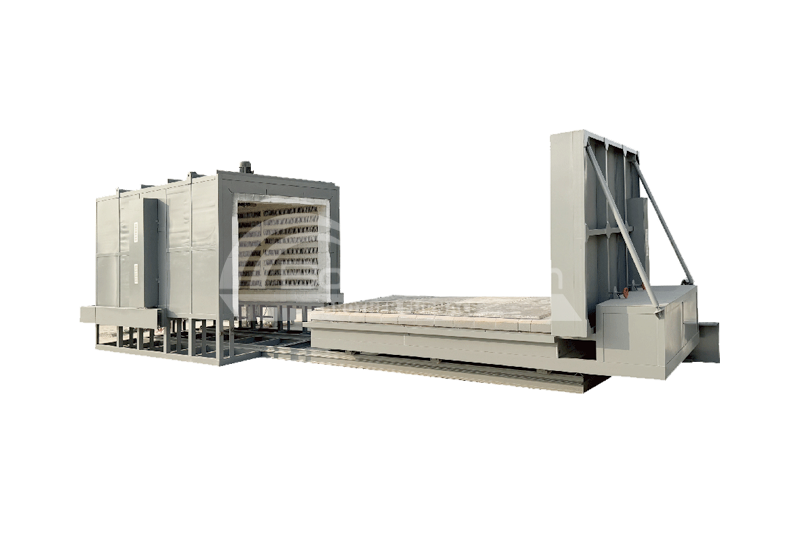
Brother Furnace Vacuum Furnace
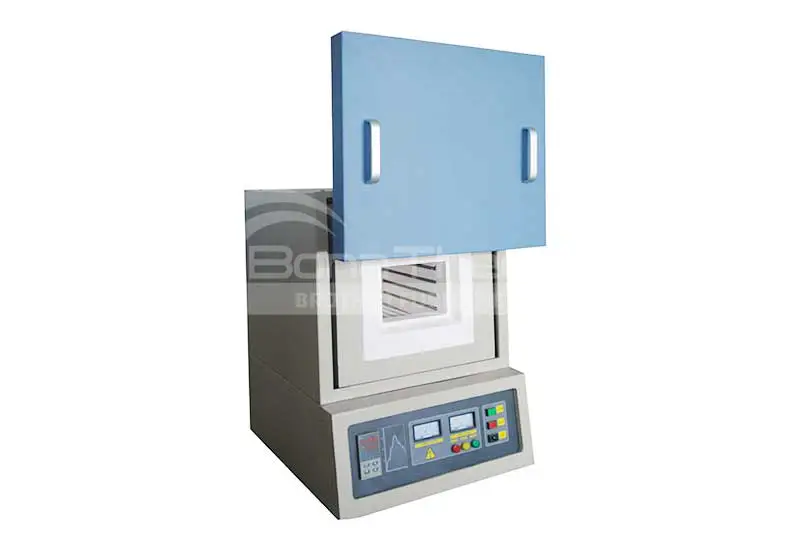
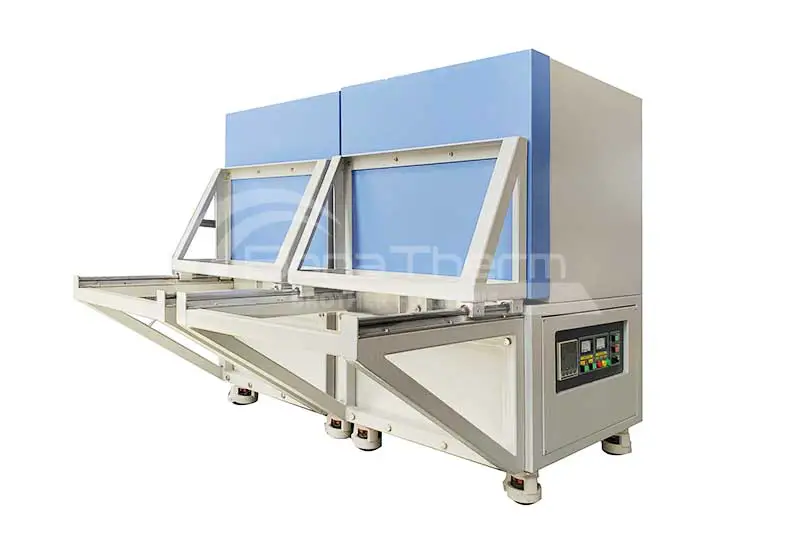
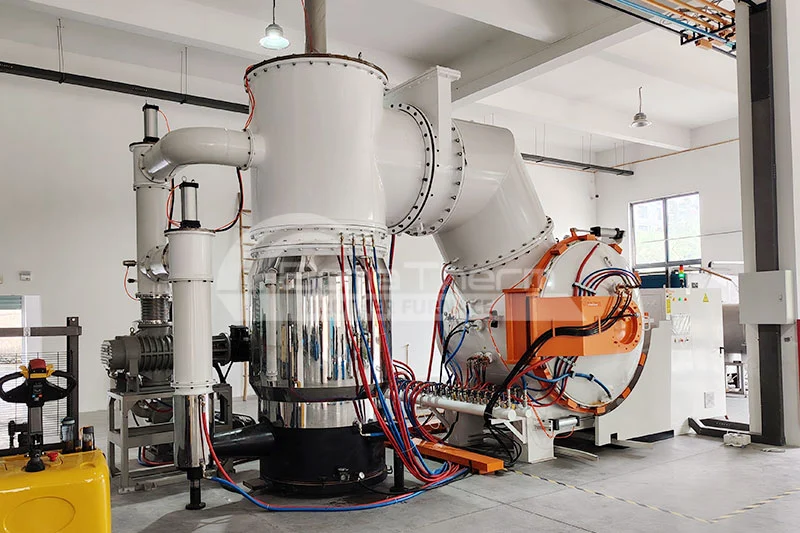
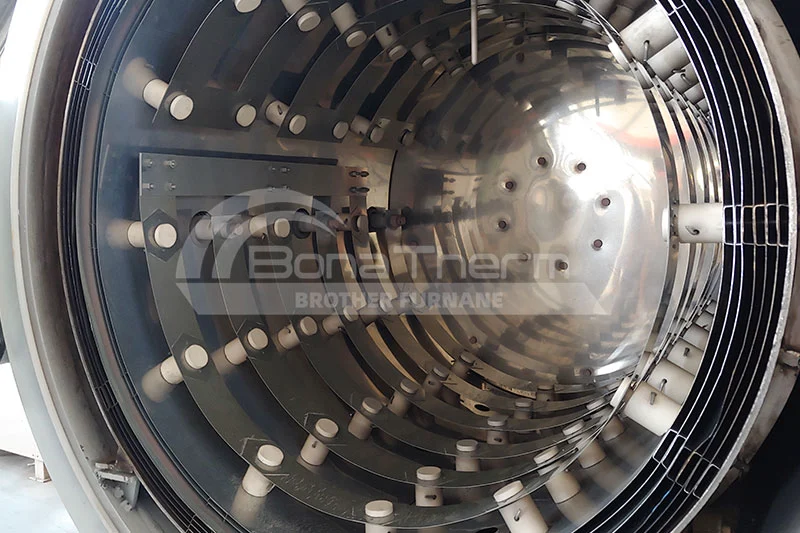
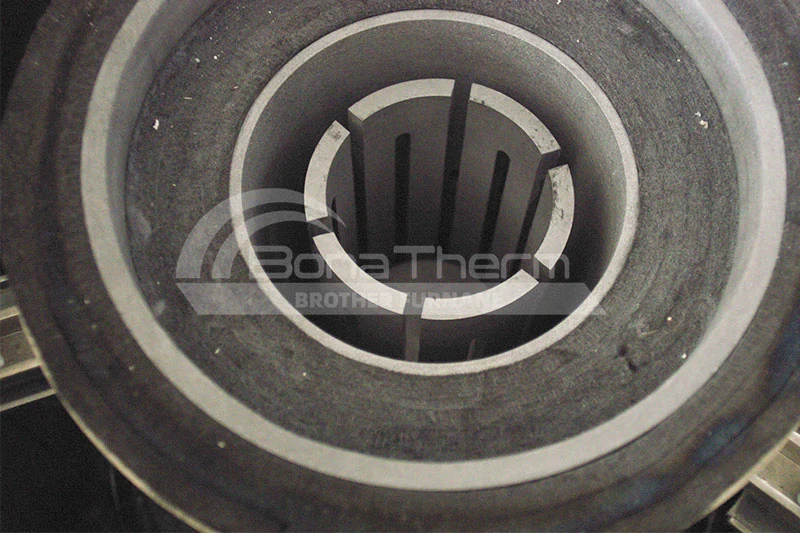
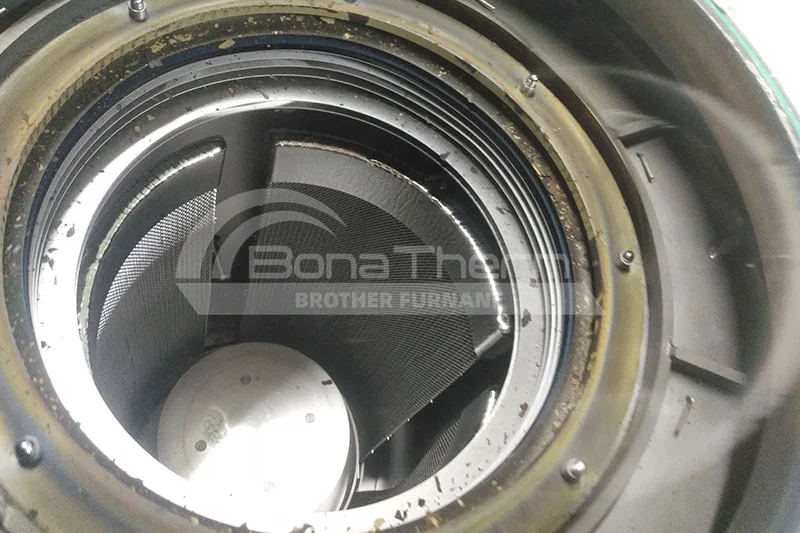
Vacuum furnaces (ceramic fiber thermal field) can use resistance wires, silicon molybdenum rods, and other heating elements depending on the temperature. Vacuum brazing furnaces (heat-resistant steel hot field) typically use alloy heating tubes to heat materials. As the name suggests, there are also vacuum furnaces (molybdenum thermal field), vacuum graphite furnaces, vacuum tungsten wire furnaces, and more, depending on the heating elements used. Click vacuum furnace to learn more about the different types of vacuum furnaces.
Conclusion
Brother Furnace is committed to developing the best vacuum furnaces for domestic and international clients. If you are looking for a vacuum furnace for your business, do not miss Brother Furnace. Should you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.