Guide to Vacuum Quenching Furnaces
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-07-18 22:41
2024-07-18 22:41
A vacuum quenching furnace is a piece of equipment used for the heat treatment of metals, enabling quenching processes in a vacuum environment to improve material strength and durability. Its importance lies in its ability to significantly reduce oxidation and decarburization on the metal surface, thereby enhancing the quality of the processed products. This article provides a detailed overview of vacuum quenching furnaces.

What is Quenching?
Quenching is a metal heat treatment process that involves heating the metal to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling it to change its internal structure, thereby increasing its hardness and strength. This process is commonly used for steel and other alloy materials to enhance their mechanical properties and wear resistance.
Working Principle of Vacuum Quenching Furnaces
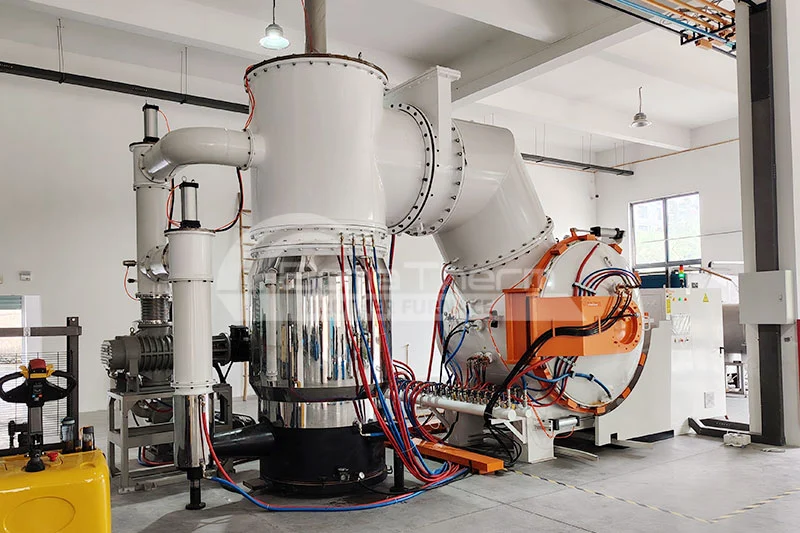
The working principle of a vacuum quenching furnace involves heating the metal workpieces inside a sealed vacuum chamber to a predetermined high temperature, then rapidly introducing a cooling medium (such as inert gas or oil) for quick cooling. The entire process takes place in a low-pressure or vacuum environment, preventing oxidation and decarburization of the metal at high temperatures.
The heating phase typically employs resistance heating or induction heating to ensure uniform and precise temperature control. During the cooling phase, the flow and pressure of the cooling medium are controlled to achieve rapid cooling, thereby imparting the desired hardness and mechanical properties to the metal.
Applications of Vacuum Quenching Furnaces
Vacuum quenching furnaces are widely used in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, precision instruments, and tool manufacturing industries. These sectors demand high hardness and durability for metal parts, which necessitates the use of vacuum quenching processes to ensure superior performance. Additionally, vacuum quenching furnaces are suitable for processing high-performance alloys and special materials that are prone to oxidation and degradation under conventional quenching processes. Using vacuum quenching effectively prevents these issues.
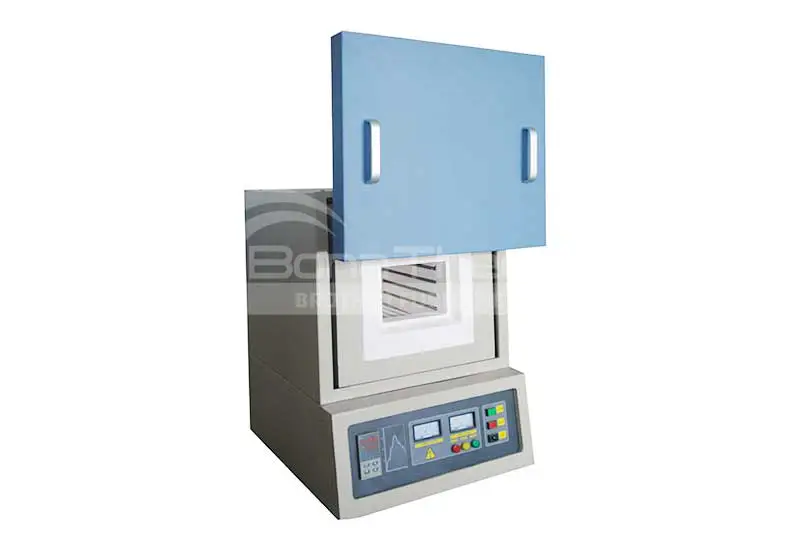
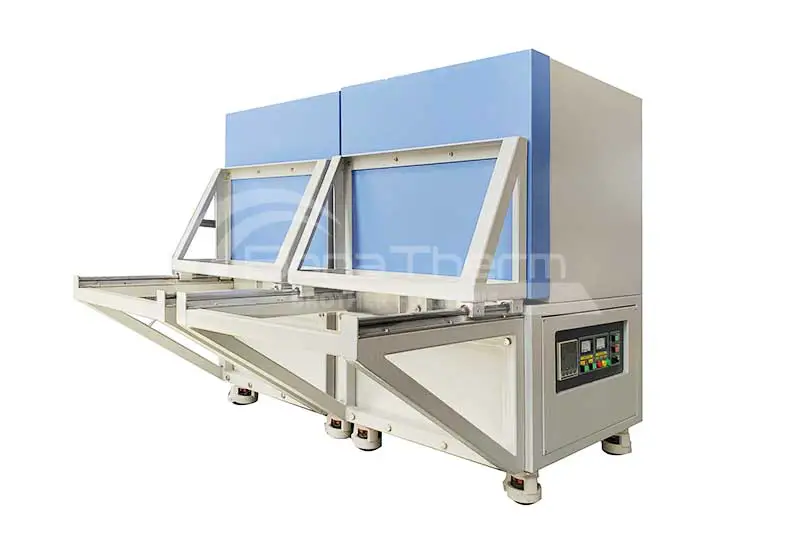
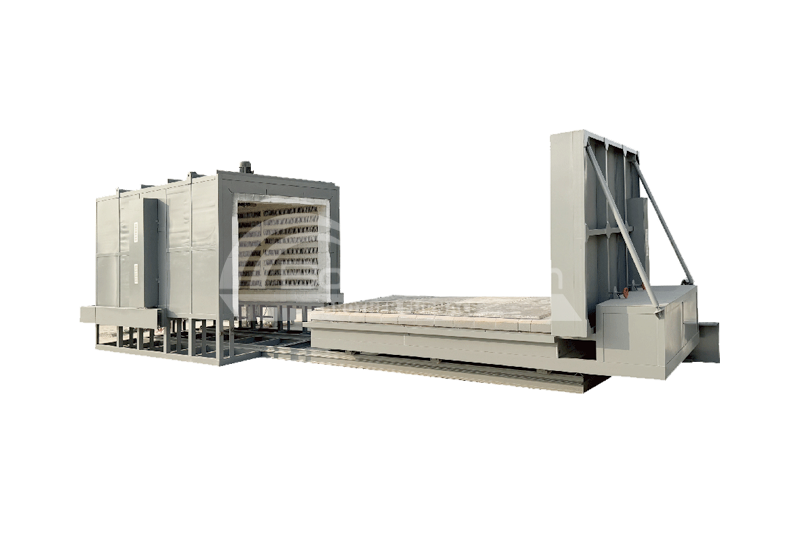
Brother Furnace's Vacuum Quenching Furnaces
Brother Furnace offers vacuum quenching furnaces known for their high precision and reliability. The company's equipment features advanced control systems and efficient cooling technologies, capable of meeting the requirements of various complex processes. Brother Furnace's vacuum quenching furnaces are also energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, easy to operate, and have low maintenance costs, making them an ideal choice for many industrial applications.
Types of Vacuum Quenching Furnaces
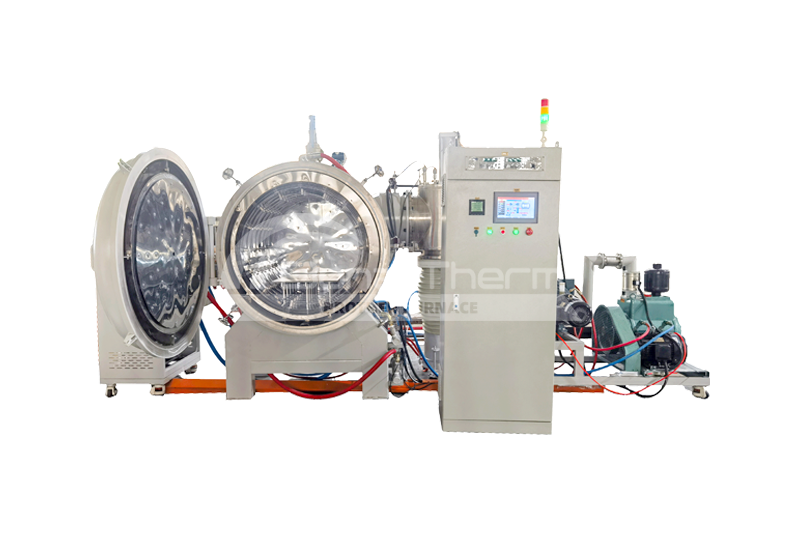
Conventional vacuum quenching furnaces include gas quenching furnaces and oil quenching furnaces, with operating temperatures reaching up to 1400°C. The primary difference between them lies in the cooling medium used.
· Vacuum Gas Quenching Furnace: Uses gases (such as nitrogen, argon, hydrogen, or helium) as the cooling medium. The gas contacts the workpiece through spraying or forced convection to achieve rapid cooling.
· Vacuum Oil Quenching Furnace: Uses cooling oil (such as mineral oil or synthetic oil) as the cooling medium. The workpiece is cooled by spraying or immersing it in the oil.
This comprehensive guide provides essential information on vacuum quenching furnaces, covering their principles, applications, and specific types available from Brother Furnace, tailored for international clients.