Application of Crystallization Technology in Tube Furnaces: From Principles to Practice
Crystallization technology plays a pivotal role in optimizing material properties across fields such as materials science, semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, and renewable energy R&D. As an indispensable thermal processing equipment in both laboratories and industrial production, tube furnaces have become the preferred solution for achieving high-quality crystallization due to their precise temperature control, adaptable chamber designs, and broad applicability. This article provides an in-depth analysis of how crystallization technology is applied in various tube furnace configurations (including horizontal, vertical, and multi-zone tube furnaces) while exploring the technical advantages of high-temperature tube furnaces and the factors influencing tube furnace prices.

Fundamentals and Process Requirements of Crystallization Technology
Definition and Significance of Crystallization
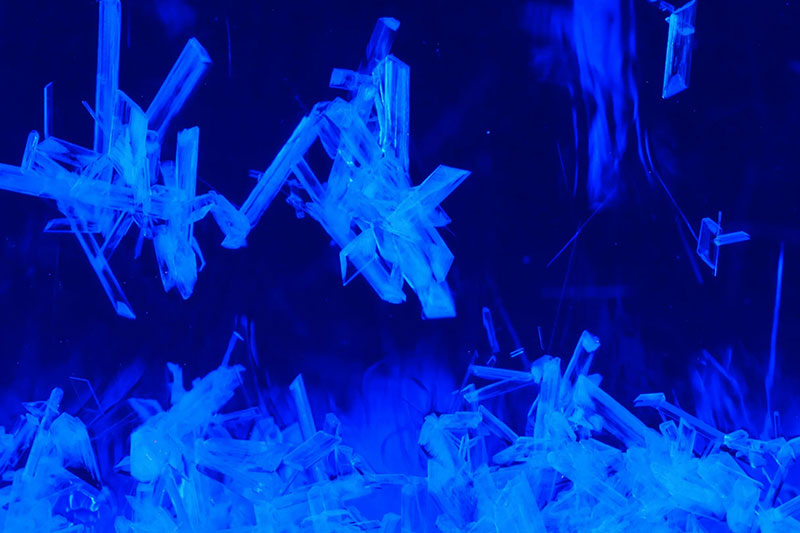
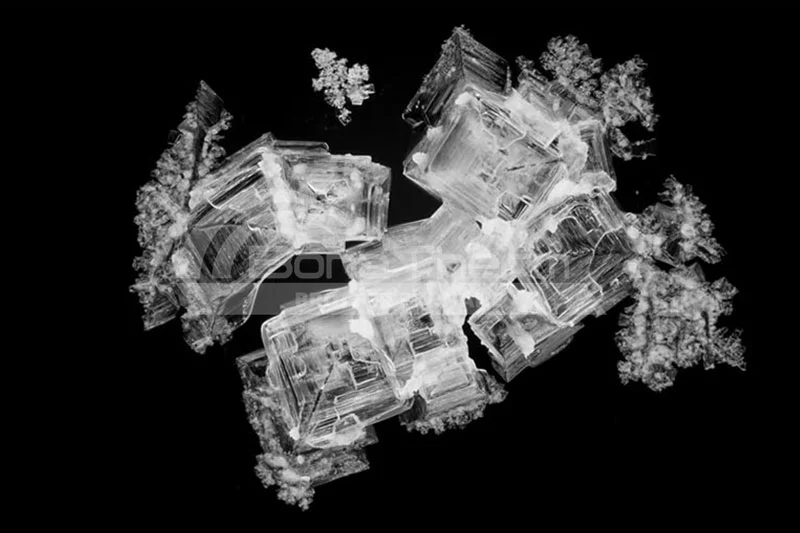
Crystallization refers to the phase transition process where substances transform from liquid, gaseous, or amorphous states into crystalline structures. The essence lies in achieving ordered atomic/molecular arrangements through temperature gradients, pressure variations, or chemical environment modulation. High-quality crystallization critically determines electrical, optical, and mechanical material properties, as exemplified in single-crystal silicon growth and metal oxide thin-film fabrication.
Equipment Requirements for Crystallization Processes
Precision temperature control: Stability within ±1°C across critical ranges (e.g., 800°C–1600°C).
Uniform heating: Elimination of thermal gradients that induce crystal defects.
Controlled atmospheres: Accurate regulation of inert (N₂, Ar) or reactive (H₂) gases.
Adaptable chamber geometry: Compatibility with diverse material loading methods and thermal field distributions.
These requirements position high-temperature tube furnaces as the optimal choice for crystallization applications.
Critical Roles of Tube Furnaces in Crystallization Processes
Structural Components of Tube Furnaces
A standard tube furnace comprises heating elements (resistance wires, silicon carbide rods), insulation layers (ceramic fiber), quartz/metal alloy tubes, temperature control systems, and gas delivery modules. Modular designs allow selection between horizontal tube furnaces (for batch processing) and vertical tube furnaces (for directional crystal growth), with expandability to multi-zone tube furnaces for complex thermal profiles.
Technical Advantages of High-Temperature Tube Furnaces
Exceptional thermal stability: Capable of reaching 1800°C for melting and recrystallization processes.
Advanced atmosphere control: Integrated vacuum pumps and mass flow controllers enable oxidation, reduction, or inert environments.
Energy efficiency: Optimized insulation minimizes heat loss and reduces cycle times.
Application Scenarios Across Tube Furnace Types
Horizontal Tube Furnaces
Typical applications:
Bulk material processing (e.g., grain refinement in powder metallurgy).
Continuous production via automated feeding systems (pusher rods/conveyor belts).
Advantages: User-friendly operation, ideal for lab-scale R&D and pilot studies.
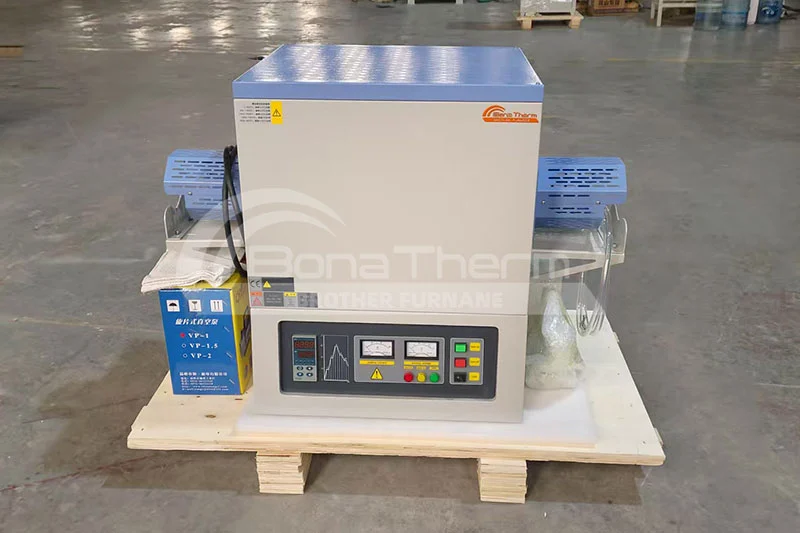

Vertical Tube Furnaces
Typical applications:
Vertical crystal growth (e.g., Czochralski method for sapphire single crystals).
Substrate-oriented thin-film deposition (e.g., chemical vapor deposition, CVD).
Advantages: Reduced contamination risks and enhanced thermal uniformity.
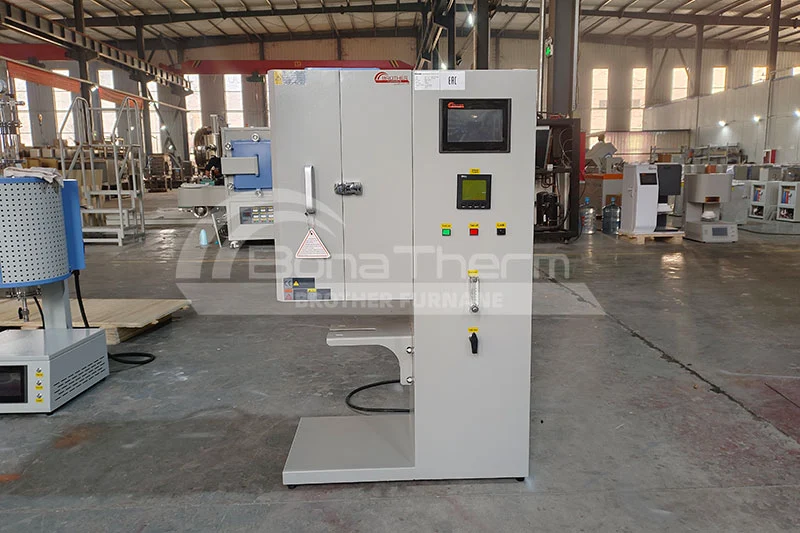

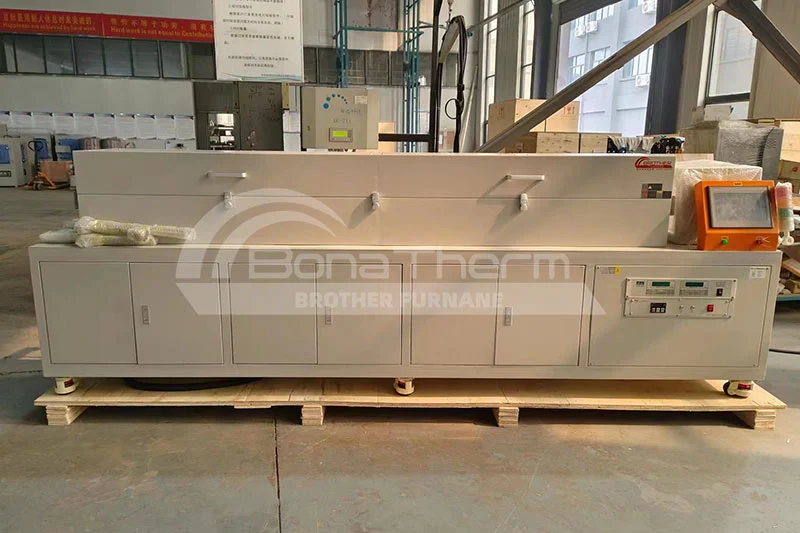
Multi-Zone Tube Furnaces
Typical applications:
Gradient crystallization (e.g., dopant concentration profiling in semiconductors).
Stepwise annealing for lattice structure optimization.
Advantages: Multi-process compatibility and unparalleled process flexibility.

Factors Influencing Tube Furnace Prices and Selection Guidelines
Key Determinants of Tube Furnace Prices
Temperature capability: High-temperature tube furnaces (>1200°C) command premium pricing.
Heating zone configuration: Multi-zone systems incur higher costs due to complex control requirements.
Material compatibility: Quartz tubes (corrosion-resistant) cost more than stainless steel alternatives.
Brand and support: Imported brands (Carbolite, Thermo Scientific) offer reliability at a price premium.
Strategies for Cost-Effective Procurement
Define process parameters: Prioritize maximum temperature, atmosphere, and sample dimensions.
Balance functionality and budget: Opt for standard horizontal models in labs vs. multi-zone systems for production.
Evaluate lifecycle costs: Prioritize models with replaceable heating elements and standardized parts.
Case Studies: Crystallization Technology in Action
Case 1: Silicon Carbide (SiC) Single Crystal Growth
Equipment: 1600°C vertical tube furnace (H₂ atmosphere).
Process: Sublimation-condensation growth on seed crystals.
Result: Crystal defect density reduced to <10²/cm².
Case 2: Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Material Synthesis
Equipment: Three-zone tube furnace with independent temperature control.
Process: Precursor decomposition (high zone), crystallization (mid zone), and annealing (low zone).
Result: Specific capacity increased to >180mAh/g.
Future Trends: Smart and Sustainable Tube Furnace Technologies
AI-driven thermal control: Machine learning algorithms optimize heating cycles, reducing energy consumption.
Green energy integration: Solar power and waste heat recovery systems minimize carbon footprint.
IoT-enabled monitoring: Real-time remote diagnostics via cloud connectivity.
Conclusion
As a cornerstone of crystallization technology, tube furnace performance directly governs material quality. Whether prioritizing the versatility of horizontal tube furnaces, the thermal homogeneity of vertical tube furnaces, or the multifunctionality of multi-zone tube furnaces, users must align equipment selection with technical requirements and tube furnace price considerations. With ongoing advancements, high-temperature tube furnaces will continue to drive innovation in materials science, enabling unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Contact our technical team today to explore tailored tube furnace solutions and request a detailed quotation!