What Materials can Dental Furnace be Used to Process?
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-01-03 00:19
2024-01-03 00:19
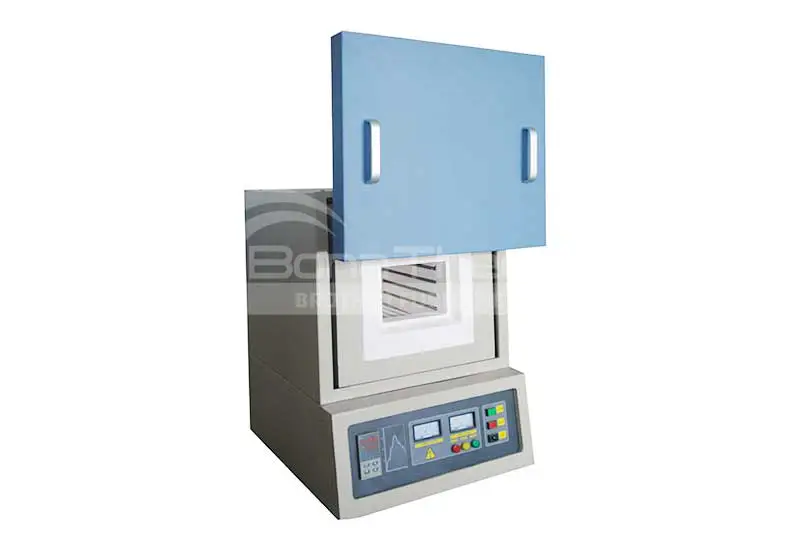
The dental furnace is an indispensable and important experimental equipment in laboratories, universities, scientific research laboratories, and the medical industry. It is mainly used to process small batches of laboratory samples such as zirconia denture crystals, structural ceramics, and polymer ceramics.
Materials that the dental furnace can process
Dental Ceramics:
Dental furnaces are commonly employed for porcelain and ceramic materials, essential for crafting crowns, bridges, and veneers. Precise heating is applied to achieve proper sintering and enhance aesthetic properties.
Metal Alloys:
Dental furnaces handle metal alloys like cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) and diverse dental gold alloys. These alloys are pivotal for producing metal substructures in dental restorations.
Zirconia:
Zirconia, known for its strength and aesthetic qualities in dental crowns and bridges, undergoes sintering and crystallization in dental furnaces at specific temperatures.
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate):
Dental furnaces contribute to the curing or polymerization of PMMA, a resin employed in temporary crowns, bridges, and provisional restorations.
Wax:
Dental furnaces are utilized for wax elimination, a crucial step in the dental casting process where wax patterns are burned out to create mold cavities for metal or ceramic restorations.
Glass Ceramics:
Glass ceramics like lithium disilicate benefit from dental furnace processing to attain the desired strength and aesthetics, commonly used in all-ceramic restorations.
Composite Resins:
Some dental furnaces accommodate the polymerization of composite resins, integral in the creation of dental restorations.
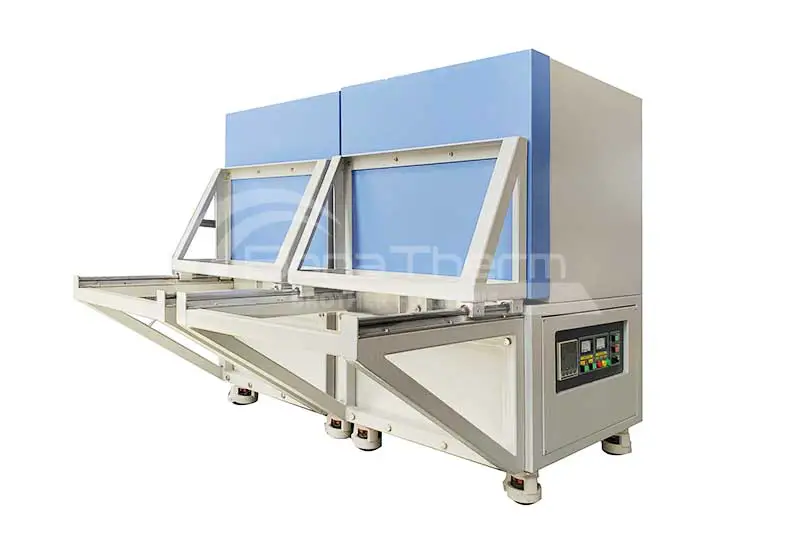
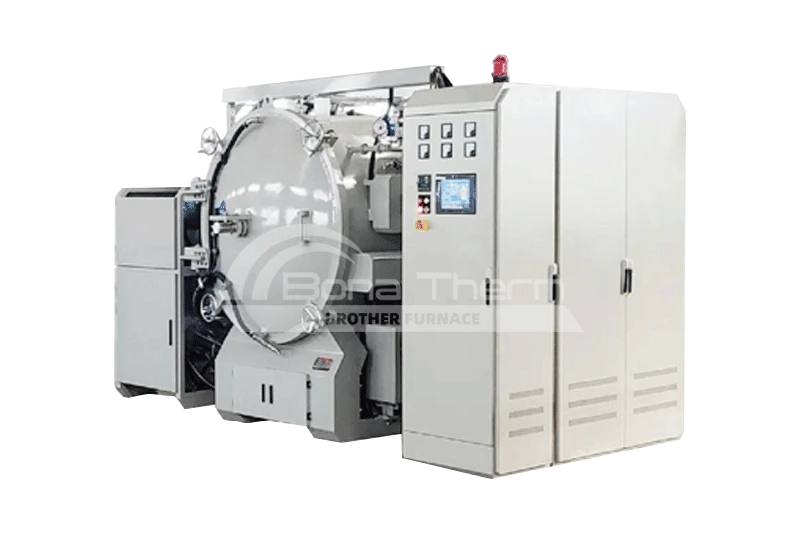
Types of Brother Furnace dental furnaces
Brother Furnace is good at producing various models of dental furnaces, mainly including four models: T-crystal, T-bright, T-bright plus, and T-run, has excellent thermal insulation performance and high temperature resistance, ensuring the temperature stability of the sample during the sintering process.