Comparison of Muffle Furnace and Tube Furnace
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-08-27 23:03
2024-08-27 23:03
In laboratory and academic research settings, muffle furnaces and tube furnaces are two indispensable high-temperature devices. They are widely used in material heat treatment, chemical experiments, and various preparation processes. Although these two furnaces share some functional similarities, their unique structures and applications make them suitable for different experimental scenarios.
By reading this article, you will gain a more detailed understanding of these two types of equipment.
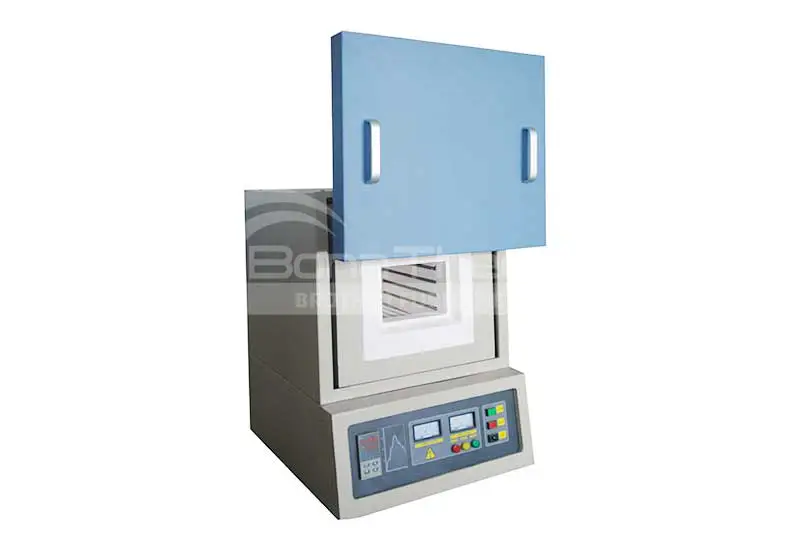
What is Muffle Furnace
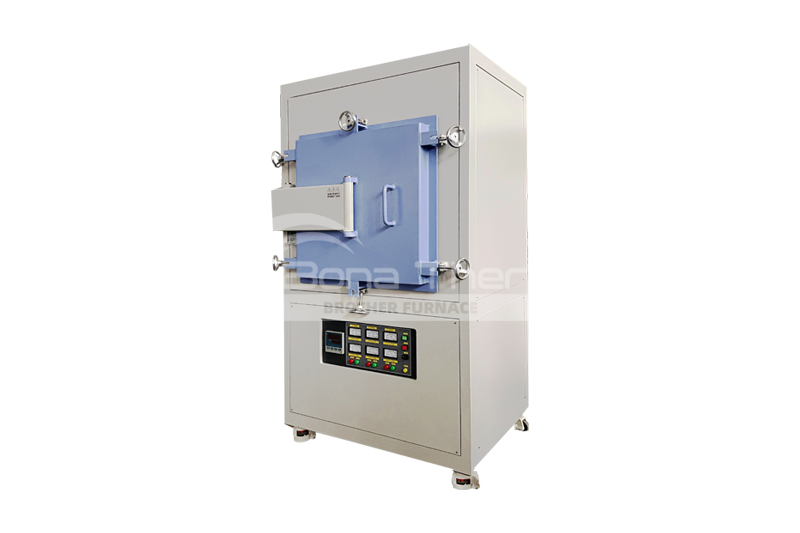
Muffle furnace is a common high-temperature furnace primarily used for heat treatment, sintering, and ashing processes in laboratories. Due to its enclosed chamber design, it is also known as a muffle oven, box furnace, or chamber furnace. It provides a uniform and stable high-temperature environment, ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of experimental results. |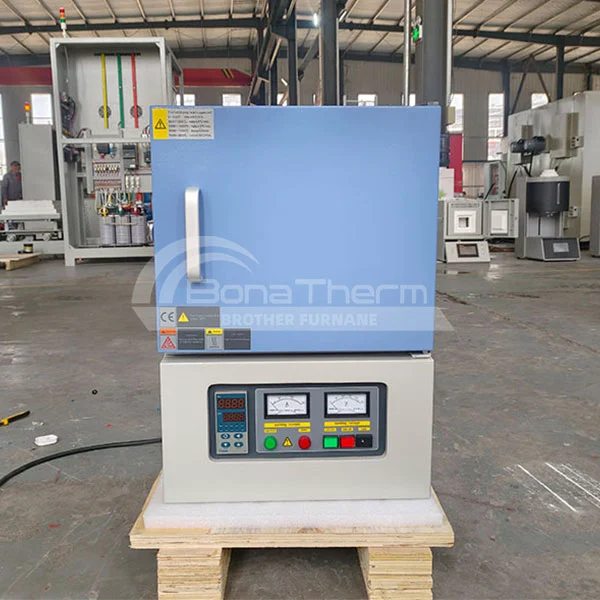  |
Structure of Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace typically consists of a sealed chamber made of ceramic or other high-temperature-resistant materials. The heating elements (resistance wire, molybdenum disilicide rods, or silicon carbide rods) are arranged around the chamber to ensure uniform heating of the samples. The outer shell is made of steel or other insulating materials, ensuring operational safety.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
The muffle furnace converts electrical energy into heat energy through its heating elements, evenly raising the temperature inside the chamber. Due to its enclosed design, heat is effectively retained within the chamber, allowing precise temperature control for the samples.
Advantages of Muffle Furnace
Temperature Uniformity: The muffle furnace provides extremely uniform chamber temperature, contributing to the stability of experimental results.
Operational Safety: The enclosed structure and good insulation make the operation process safer.
Versatile Applications: Suitable for various experiments, including material heat treatment, ashing, and sintering.
Common Uses of Muffle Furnace
Material Heat Treatment: Used for heat treatment and sintering of metals, ceramics, and other materials.
Ashing Experiments: Employed to determine the organic content in samples.
Chemical Reactions: Suitable for chemical experiments requiring stable high temperatures.
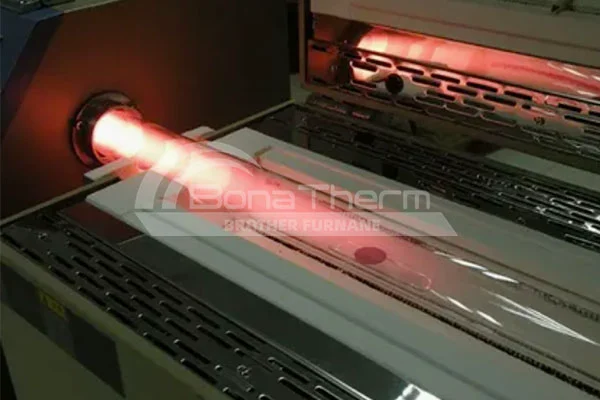

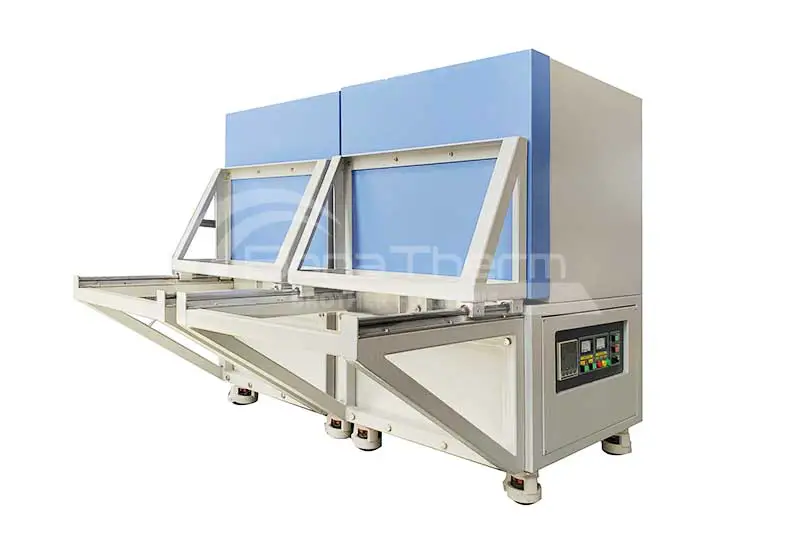
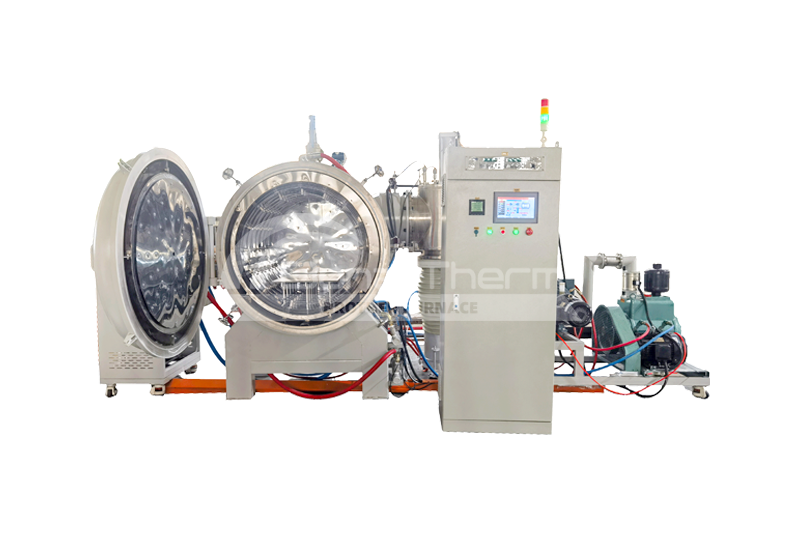
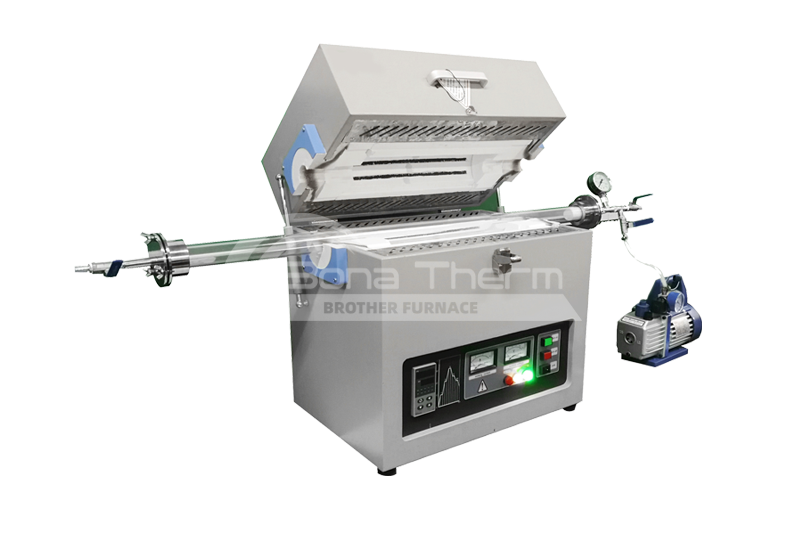
What is Tube Furnace?
Tube furnace is a specialized high-temperature device typically used in experiments that require precise atmosphere control, such as material synthesis and crystal growth. It is characterized by a long, narrow chamber with a tubular design running through it, allowing for flexible adjustment of internal atmosphere conditions. |  |
Structure of Tube Furnace
The core of a tube furnace is a long cylindrical chamber equipped with heating elements. Samples are usually placed in a high-temperature-resistant quartz or ceramic tube that runs through the entire chamber. The ends of the chamber can be connected to gas flow systems to control the experimental atmosphere. Tube furnaces can be designed in horizontal, vertical, or rotary configurations and can be multi-zone tube furnaces depending on temperature requirements.
How a Tube Furnace Works
A tube furnace directly heats the atmosphere or samples inside the chamber through its heating elements, transferring heat from the chamber walls to the interior of the tube. The open design allows the tube furnace to flexibly control the internal atmosphere, adapting to different experimental needs.
Advantages of a Tube Furnace
Precise Atmosphere Control: Can be connected to gas systems for precise control of the experimental atmosphere.
Temperature Gradient Control: Suitable for experiments requiring temperature gradients, such as crystal growth.
Wide Applicability: Capable of handling long or specially shaped samples, catering to a wide range of experimental needs.
Common Uses of a Tube Furnace
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Used in the semiconductor industry for thin film deposition.
Material Synthesis: Conducts material synthesis experiments under high-temperature conditions.
Crystal Growth: Ideal for crystal growth experiments requiring temperature gradient control.
Conclusion
Muffle furnaces and tube furnaces each have their advantages in the field of scientific research. Muffle furnaces are widely used for their temperature uniformity and versatility, particularly in material heat treatment and analytical experiments. On the other hand, tube furnaces are preferred for their excellent atmosphere control and ability to conduct experiments with temperature gradients, making them ideal for material synthesis and specific chemical reactions.
With years of experience in producing laboratory furnaces, Brother Furnace can recommend and design the most suitable furnace based on your specific experimental requirements and sample characteristics.
If you are looking for the right furnace for your business, feel free toleave us a message. We will respond within an hour!