-
How Vacuum Brazing Furnaces are Redefining the Limits of Stainless Steel Manufacturing
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE 18 Feb,2025
18 Feb,2025
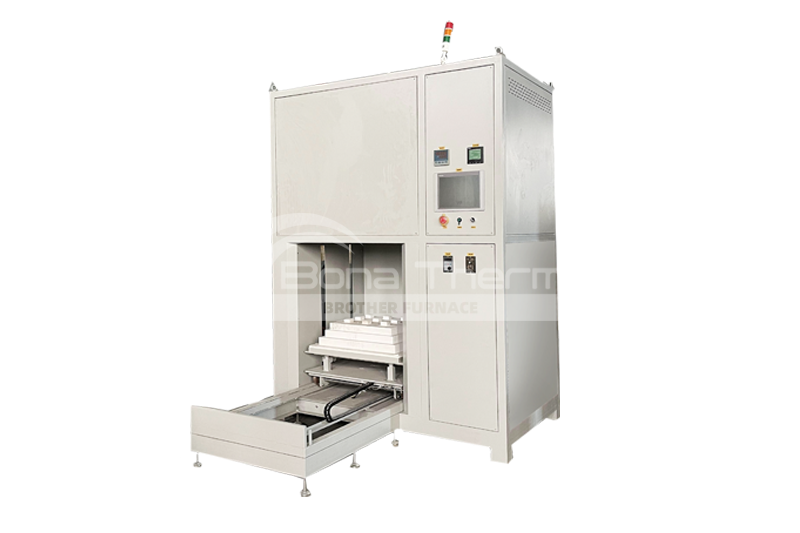
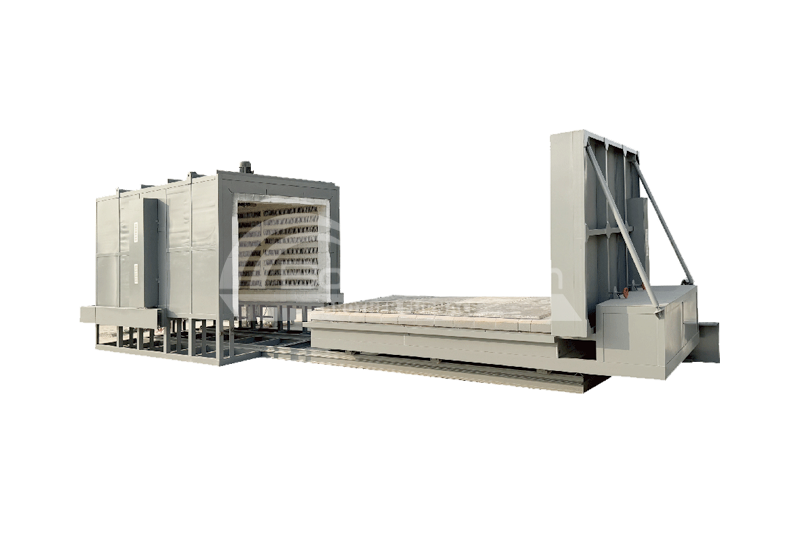
In manufacturing aerospace pipelines, medical devices, and nuclear equipment, the quality of the connections of stainless steel components directly determines the product's lifespan and safety.
VIEW MORE >> -
2025 Spring Festival Holiday Notice
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE 23 Jan,2025
23 Jan,2025
Dear Valued Customers, We want to express our sincere gratitude for your continued support and trust in Brother Furnace. As the Chinese Spring Festival approaches, we wish to inform you that our
VIEW MORE >> -
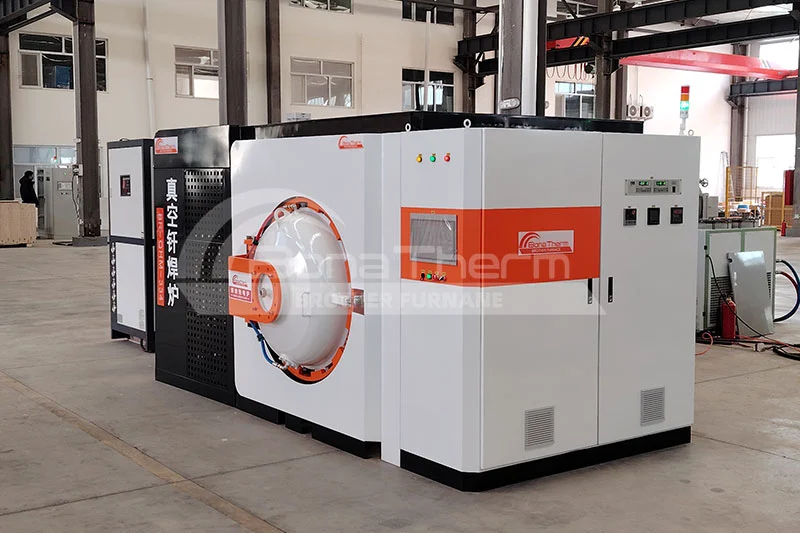
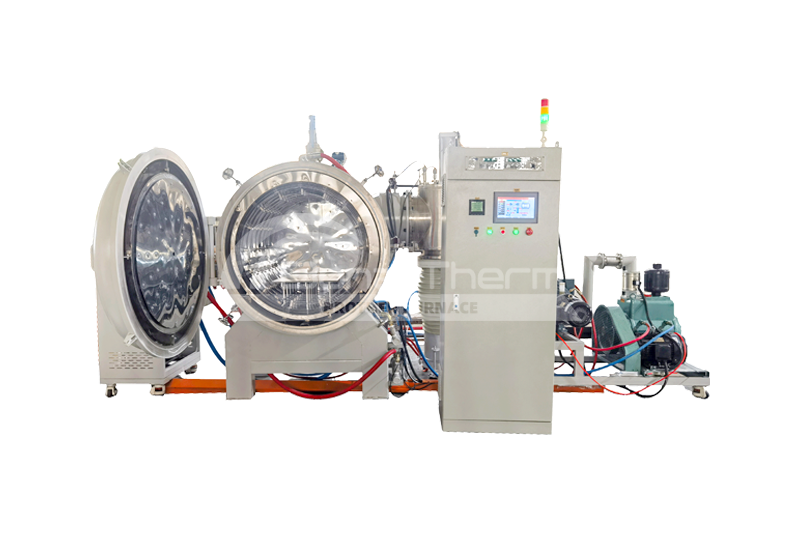
Advantages of Stainless Steel Vacuum Brazing Furnaces
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE 15 Jan,2025
15 Jan,2025
Brazing furnaces play a critical role in modern industrial production. Industries such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, electronics, and medical devices heavily rely on brazing technology. Vacuum brazing, in particular, has become a preferred method due to its high precision and superior quality.
VIEW MORE >> -
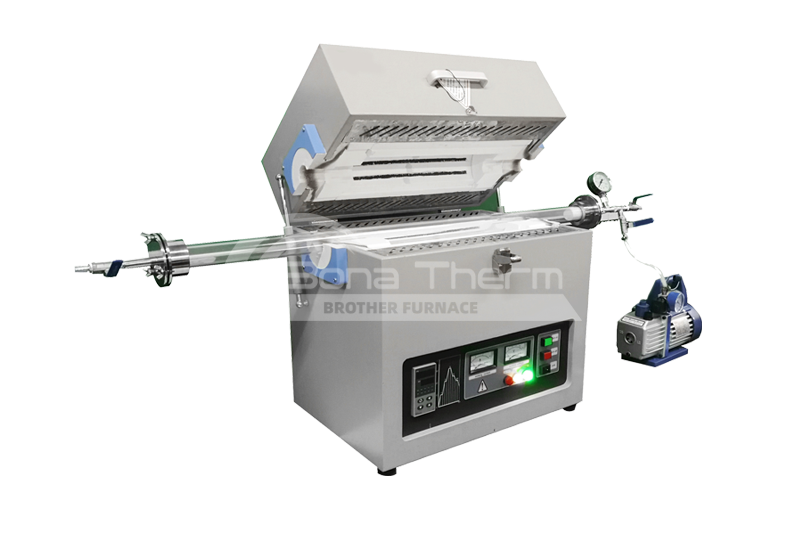
The Applications of Continuous Vacuum Furnaces in Metal Heat Treatment
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE 25 Dec,2024
25 Dec,2024
In modern industrial production, the continuous vacuum furnace has become one of the most important devices for metal heat treatment. With advancements in technology, the application scope of continuous vacuum furnaces has expanded, particularly with the support of equipment such as vacuum brazing and vacuum sintering furnaces
VIEW MORE >> -
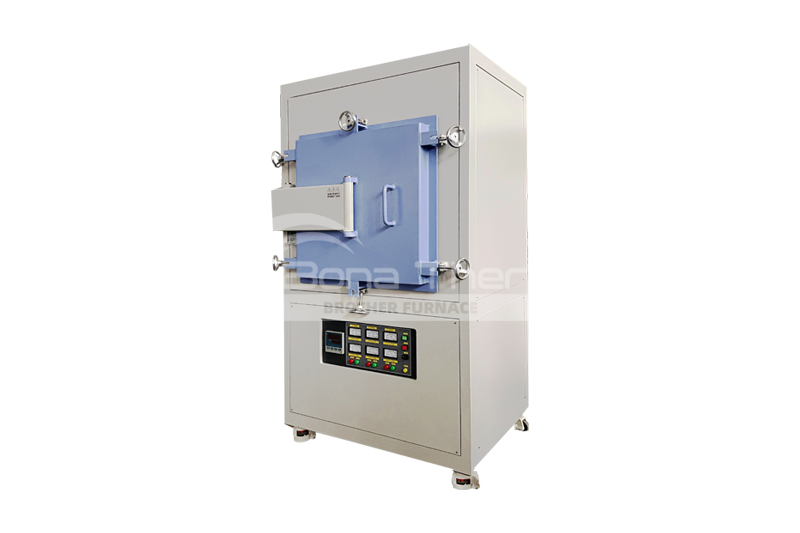
The Application and Advantages of Titanium Alloys in Vacuum Brazing Furnaces
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE 18 Dec,2024
18 Dec,2024
Titanium alloys, renowned for their exceptional mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and lightweight characteristics, are widely used in numerous high-demand industries. To meet the welding requirements of titanium alloys, vacuum brazing technology has become a crucial method for precise joining. This article will provide a detailed overview of the applications and advantages of titanium alloys, particularly in vacuum brazing processes.
VIEW MORE >> -
Vacuum Furnaces: Key Applications in the Aerospace Industry
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE 12 Dec,2024
12 Dec,2024
In the aerospace industry, aircraft and spacecraft demand exceptional material properties and precision in component manufacturing. Even the slightest defect can compromise performance and safety.
VIEW MORE >>
- Home
- Products
- Vacuum Furnace
-
Muffle Furnace
- 200℃-1800℃ Laboratory Box Muffle Furnace
- Box Muffle Furnace up to 1200℃
- Box Muffle Furnace up to 1400℃
- Box Muffle Furnace up to 1700℃
- Box Muffle Furnace up to 1800℃
- Industrial Muffle Furnace
- Muffle Ashing Furnace
- Controlled Atmosphere Muffle Furnace
- Crucible Muffle Furnace
- Muffle Furnace with Observation Window
- Double Door Muffle Furnace
- Dental Muffle Furnace
- PC-Controlled Muffle Furnace
- Customized Box/Muffle Furnace
-
Tube Furnace
- Horizontal Tube Furnace
- Vertical Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace
- Slide-Rapid Cooling Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Multi-Station Tube Furnace
- CVD/PECVD Tube Furnace
- (Double/three/five temperature zones)Multi-Temperature Zone Tube Furnace
- Double-Tube Tube Furnace
- Customized Tube Furnace
-
Atmosphere Furnace
- Atmosphere Furnace up to 1700℃
- Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- External Heating Atmosphere Furnace
- Atmosphere Hot Press Furnace
- 1400°C Touchscreen Atmosphere Furnace (200×200×200 mm)
- Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200°C Atmosphere Furnace (400×400×400 mm)
- Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400°C Atmosphere Furnace (300×300×300 mm)
- 1200°C Atmosphere Furnace (200×200×300 mm)
- Debinding and Sintering Furnace
- Lifting Bottom Furnace
- Bogie Hearth Furnace
- Dental Furnace
- Application
- Case
- Blog
- About
- Contact