Alumina Tube Furnace or Quartz Tube Furnace? How to Choose the Right Furnace
 BROTHER FURNACE
BROTHER FURNACE
 2024-11-05 19:41
2024-11-05 19:41
In high-temperature heat treatment and laboratory applications, tube furnaces are essential tools. Among the most common types are alumina and quartz tube furnaces, each with distinct characteristics and advantages. Widely used in fields such as materials science, chemical experimentation, and heat treatment, these two furnace types meet various needs. This article explores the characteristics, differences, and applications of alumina and quartz tube furnaces to help you make an informed choice.

Introduction of Alumina Tube Furnaces
Alumina (Al2O3) is a material known for its excellent high-temperature stability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace tubes. Alumina tube furnaces typically withstand temperatures ranging from 1000℃ to 1600℃, making them suitable for experiments and processes requiring extended high-temperature operations. With its high hardness and chemical resistance, alumina is a popular choice for handling gases that contain acidic or alkaline components, making it widely used in both laboratories and industrial settings.
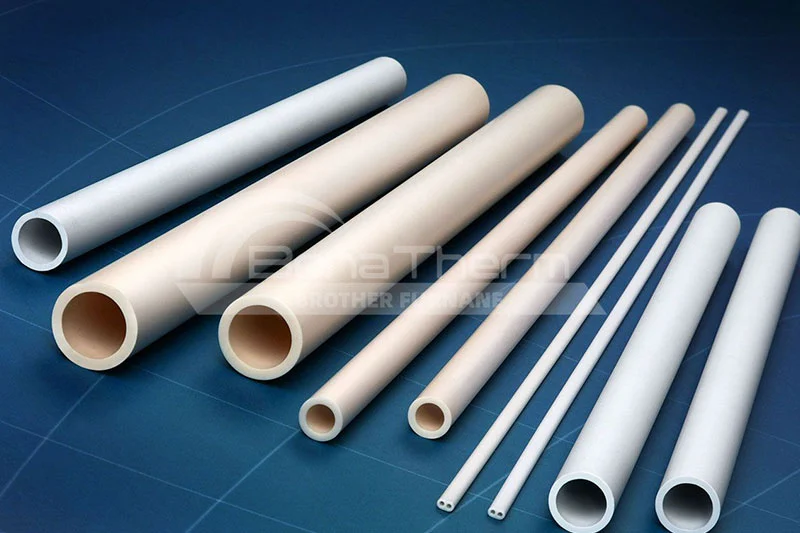

Advantages of Alumina Tube Furnaces
High-Temperature Resistance:
Alumina tube furnaces are suitable for temperatures between 1000℃ and 1600℃, covering the needs of most laboratory and heat treatment applications.
Corrosion Resistance:
Alumina offers strong resistance to chemical corrosion, making it compatible with acidic and alkaline gas applications.
Durability:
Alumina tubes have high hardness and a long service life, allowing them to withstand rigorous experimental conditions.
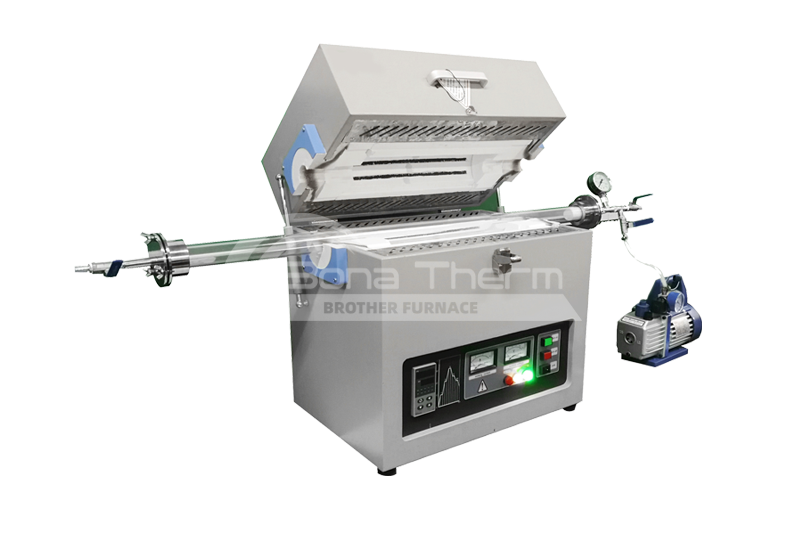
Introduction of Quartz Tube Furnaces
Quartz is a transparent material with excellent thermal stability and optical clarity. Quartz tube furnaces perform well in low to medium temperature ranges (800℃ to 1200℃), making them ideal for applications requiring visual monitoring during heating. With a low thermal expansion coefficient, quartz has excellent thermal shock resistance and is particularly suited to experiments involving frequent temperature fluctuations.
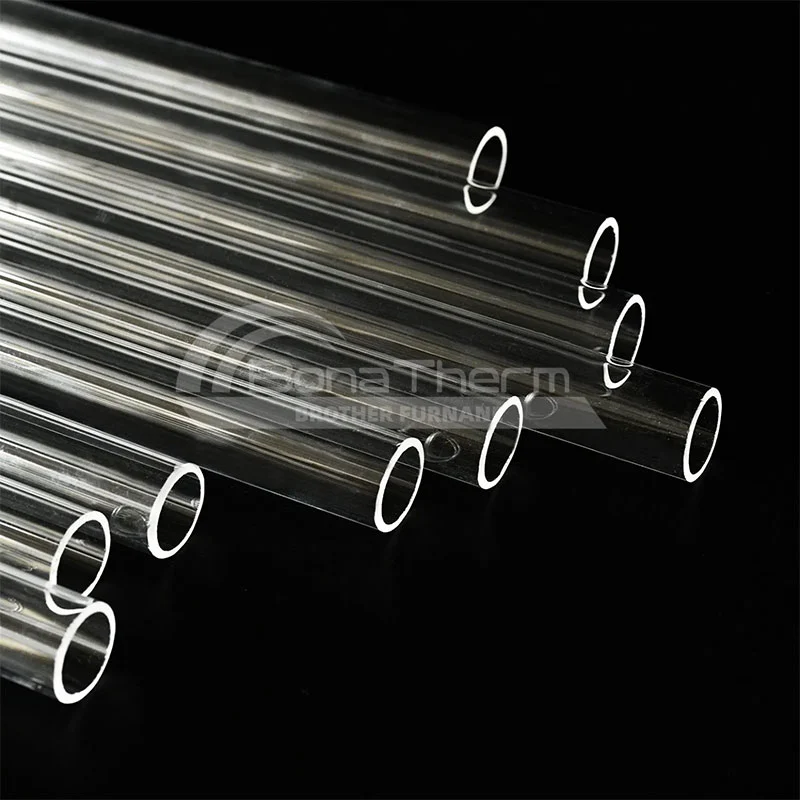

Advantages of Quartz Tube Furnaces:
Optical Clarity:
The transparency of quartz allows for visual monitoring of samples during the heating process, which is ideal for experiments that require real-time observation.
Thermal Shock Resistance:
With a low thermal expansion coefficient, quartz can withstand rapid temperature changes, making it suitable for fluctuating thermal environments.
Purity:
Quartz has a high purity level and is less likely to contaminate samples, making it ideal for experiments sensitive to impurities.
Key Differences Between Alumina and Quartz Tube Furnaces
| Feature | Alumina Tube Furnace | Quartz Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 1000°C - 1600°C | 800°C - 1200°C |
| Optical Clarity | Opaque | Transparent |
| Corrosion Resistance | Relatively high | Lower |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | Very strong |
| Suitability | High-temperature experiments and processes | Low- to mid-temperature experiments with real-time observation needs |
Choosing the Right Tube Furnace
1. Temperature Requirements: If the experiment requires temperatures above 1200℃, an alumina tube furnace is recommended. For lower temperature operations (800℃ to 1200℃), a quartz tube furnace is sufficient.
2. Observation Needs: For experiments requiring visual monitoring of samples during heating, the transparency of quartz tube furnaces is ideal. Alumina, on the other hand, does not meet this requirement.
3. Corrosion Resistance: If the heating process involves corrosive gases, an alumina tube furnace is more suitable due to its higher chemical resistance.
4. Budget Considerations: For budget-conscious applications with low to moderate temperature requirements, a quartz tube furnace offers a more economical option.
Conclusion
Alumina and quartz tube furnaces each offer unique advantages for different experimental requirements. When selecting a tube furnace, consider factors such as temperature range, the need for visual monitoring, sample contamination sensitivity, and budget. Alumina tube furnaces are ideal for high-temperature and corrosion-resistant needs, while quartz tube furnaces are better suited for lower-temperature applications where real-time observation is important.
If you are looking for suitable tube furnace equipment for your business, welcome to contact us Brother Furnace, we will provide you with the most suitable solution.